MySQL · myrocks · myrocks index condition pushdown
Author: 张远
index condition pushdown
Index condition pushdown(ICP)是直到mysql5.6才引入的特性,主要是为了减少通过二级索引查找主键索引的次数。目前ICP相关的文章也比较多,本文主要从源码角度介绍ICP的实现。讨论之前,我们先再温习下。
以下图片来自mariadb
-
引入ICP之前
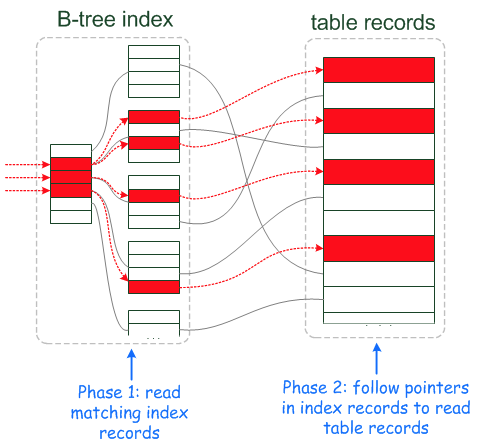
-
引入ICP之后
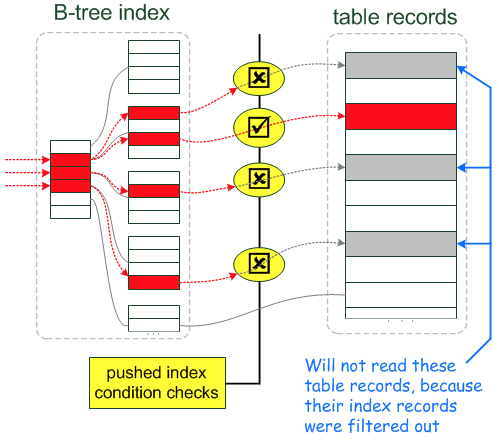
再来看个例子
CREATE TABLE `t1` (
`a` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`b` char(8) DEFAULT NULL,
`c` int(11) DEFAULT '0',
`pk` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
PRIMARY KEY (`pk`),
KEY `idx1` (`a`,`b`)
) ENGINE=ROCKSDB;
INSERT INTO t1 (a,b) VALUES (1,'a'),(2,'b'),(3,'c');
INSERT INTO t1 (a,b) VALUES (4,'a'),(4,'b'),(4,'c'),(4,'d'),(4,'e'),(4,'f');
set optimizer_switch='index_condition_pushdown=off';
## 关闭ICP(Using where)
explain select * from t1 where a=4 and b!='e';
+----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t1 | range | idx1 | idx1 | 14 | NULL | 2 | Using where |
+----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+-------------+
## 关闭ICP走cover index(Using where; Using index)
explain select a,b from t1 where a=4 and b!='e';
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+-------+------+--------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+-------+------+--------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t1 | ref | idx1 | idx1 | 5 | const | 4 | Using where; Using index |
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+-------+------+--------------------------+
set optimizer_switch='index_condition_pushdown=on';
## 开启ICP(Using index conditione)
explain select * from t1 where a=4 and b!='e';
+----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+-----------------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+-----------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t1 | range | idx1 | idx1 | 14 | NULL | 2 | Using index condition |
+----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+-----------------------+
## 开启ICP仍然是cover index(Using where; Using index)
explain select a,b from t1 where a=4 and b!='e';
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+-------+------+--------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+-------+------+--------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t1 | ref | idx1 | idx1 | 5 | const | 4 | Using where; Using index |
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+-------+------+--------------------------+
这里总结下ICP的条件
- 适用于以下类型,range, ref, eq_ref, and ref_or_null 的二级索引
- 不能是覆盖索引(cover index)
server层主要负责判断是否符合ICP的条件,符合ICP则把需要的condition push到engine层。 engine层通过二级索引查找数据时,用server层push的condition再做一次判断,如果符合条件才会去查找主索引。
目前mysql支持ICP的引擎有MyISAM和InnoDB,MyRocks引入rocksdb后,也支持了ICP。 server层实现是一样的,engine层我们主要介绍innodb和rocksdb的实现。
server层
关键代码片段如下
make_join_readinfo()
switch (tab->type) {
case JT_EQ_REF:
case JT_REF_OR_NULL:
case JT_REF:
if (tab->select)
tab->select->set_quick(NULL);
delete tab->quick;
tab->quick=0;
/* fall through */
case JT_SYSTEM:
case JT_CONST:
/* Only happens with outer joins */
if (setup_join_buffering(tab, join, options, no_jbuf_after,
&icp_other_tables_ok))
DBUG_RETURN(true);
if (tab->use_join_cache != JOIN_CACHE::ALG_NONE)
tab[-1].next_select= sub_select_op;
if (table->covering_keys.is_set(tab->ref.key) &&
!table->no_keyread)
table->set_keyread(TRUE);
else
push_index_cond(tab, tab->ref.key, icp_other_tables_ok,
&trace_refine_table);
break;
从代码中看出只有符合的类型range, ref, eq_ref, and ref_or_null 二级索引才可能会push_index_cond。
而这里通过covering_keys来判断并排除使用了cover index的情况。covering_keys是一个bitmap,保存了所有可能用到的覆盖索引。在解析查询列以及条件列时会设置covering_keys,详细可以参考setup_fields,setup_wild,setup_conds。
engine层
innodb
innodb在扫描二级索引时会根据是否有push condition来检查记录是否符合条件(row_search_idx_cond_check) 逻辑如下:
row_search_for_mysql()
......
if (prebuilt->idx_cond)
{
row_search_idx_cond_check //检查condition
row_sel_get_clust_rec_for_mysql //检查通过了才会去取主索引数据
}
....
典型的堆栈如下
handler::compare_key_icp
innobase_index_cond
row_search_idx_cond_check
row_search_for_mysql
ha_innobase::index_read
ha_innobase::index_first
ha_innobase::rnd_next
handler::ha_rnd_next
rr_sequential
join_init_read_record
sub_select
do_select
rocksdb
rocksdb在扫描二级索引时也会根据是否有push condition来检查记录是否符合条件
逻辑如下
read_row_from_secondary_key()
{
find_icp_matching_index_rec//push了condition才会检查condition
get_row_by_rowid//检查通过了才会去取主索引数据
}
典型的堆栈如下
handler::compare_key_icp
myrocks::ha_rocksdb::check_index_cond
myrocks::ha_rocksdb::find_icp_matching_index_rec
myrocks::ha_rocksdb::read_row_from_secondary_key
myrocks::ha_rocksdb::index_read_map_impl
myrocks::ha_rocksdb::read_range_first
handler::multi_range_read_next
other
ICP对cover index作出了严格的限制,而实际上应该可以放开此限制,这样可以减少enging层传第给server层的数据量,至少可以减少server层的内存使用。欢迎指正!