MySQL · 引擎特性 · Binlog encryption 浅析
Author: zhuyan
背景介绍
为了保障数据安全,MySQL 在 5.7 版本就支持了 InnoDB 表空间加密,之前写了一篇月报介绍过,参考InnoDB 表空间加密。文章开头也提到过,MariaDB 除了对表空间加密,也可以对 redo log 和 binlog 加密,本质上 redo log 和 binlog 中也保存着明文的数据,如果文件被拖走数据也有丢失的风险,因此在 MySQL 8.0 中也支持两种日志的加密,本文介绍 Binlog 的加密方式,建议先了解一下表空间加密,更容易理解。
使用方式
首先需要在 DB 启动的时候加载 Keyring,关于 Keyring 可以参考官方文档 或者上个小节提到的表空间加密的月报。
[mysqld]
early-plugin-load=keyring_file.so
控制是否对 Binlog 文件加密的开关是:binlog_encryption ,此开关可以动态打开或者关闭,修改会引起一次 Binlog rotate。需要用户具有 BINLOG_ENCRYPTION_ADMIN 权限。
mysql> set global binlog_encryption = ON;
配置完成后新的 Binlog 文件就是加密的了,加密是文件级别的,可以查看具体哪个文件被加密了:
mysql> show binary logs;
+------------------+-----------+-----------+
| Log_name | File_size | Encrypted |
+------------------+-----------+-----------+
| mysql-bin.000001 | 178 | No |
| mysql-bin.000002 | 178 | No |
| mysql-bin.000003 | 202 | No |
| mysql-bin.000004 | 714 | Yes |
| mysql-bin.000005 | 178 | No |
| mysql-bin.000006 | 178 | No |
| mysql-bin.000007 | 856 | No |
| mysql-bin.000008 | 707 | Yes |
+------------------+-----------+-----------+
原理解析
同样为了支持 Key rotate,秘钥分为 master key 和 file password, 其中 master key 保存在 keyring 中,用来加密 file password, 这样每次 key rotate 的时候,只需要用新的 master key 把所有 Binlog 文件的 file password 重新加密一遍即可。
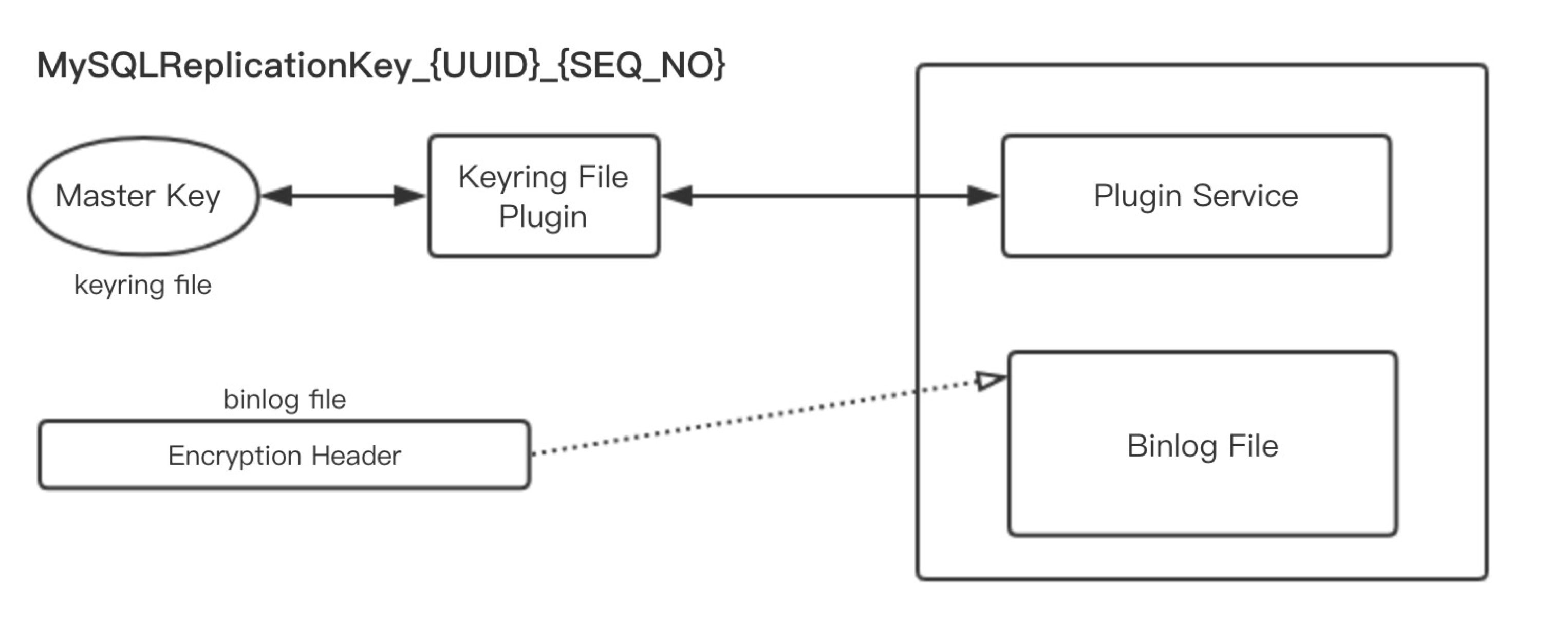
如图所示,master key 的密文是保存在 Keyring 中的,明文是固定的格式: MySQLReplicationKey_{UUID}_{SEQ_NO} , 其中 SEQ_NO 是每次 Key rotate 的时候自增的。因为由明文获得 Keyring 中的密文是不可逆的加密,因此明文简单点也不要紧,我们需要保证的是 Keyring 的安全。
filepassword 是保存在每个 Binlog 文件的头部的,文件头部新增的数据格式如下:
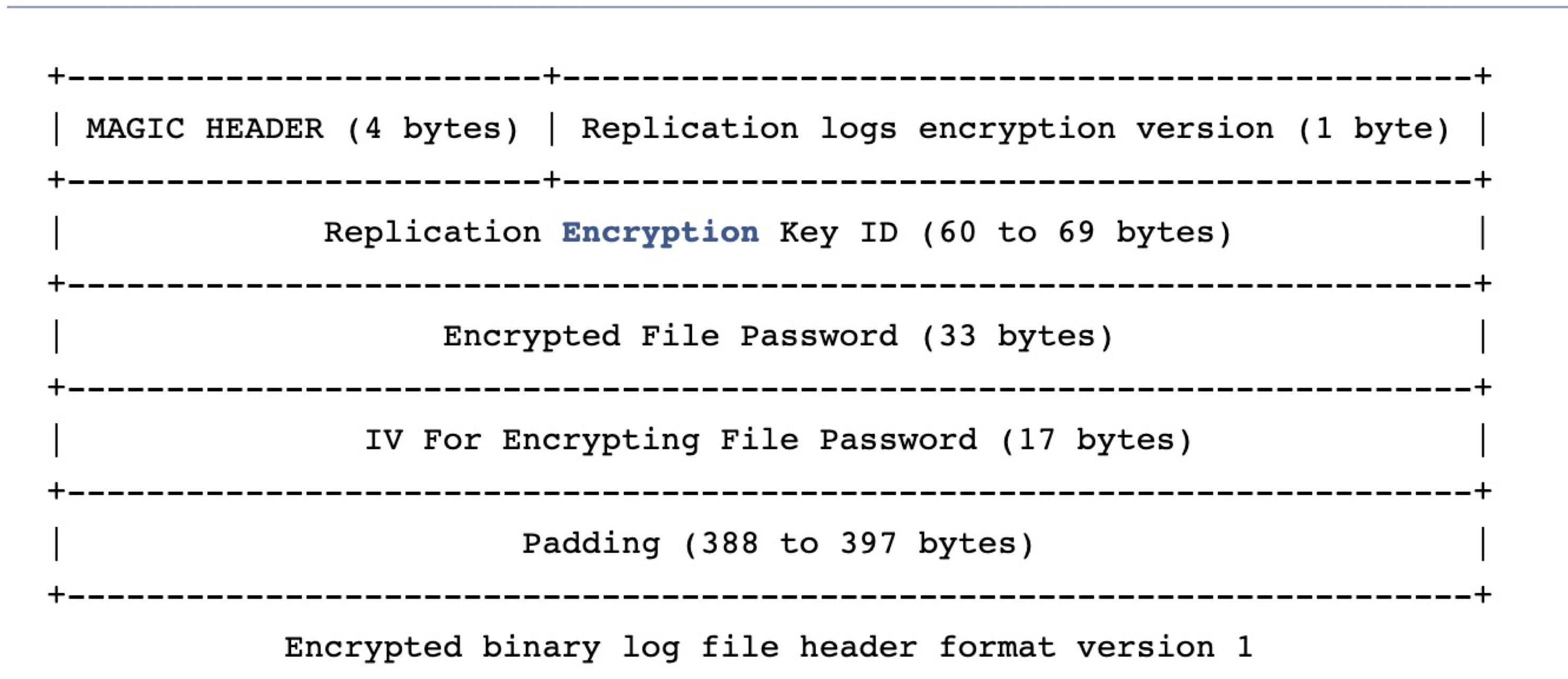
这部分是不加密的,一个文件是否加密是用 Magic num 来确定的,(0xFE62696E) 不加密, (0xFD62696E), 加密。每次打开一个文件的时候,都先判断 Magic num,确定是否需要解密。Version 不用多解释,数据格式高低版本兼容的时候用的到。Encryption Key Id 保存的就是 master key 的明文。File Password 就是加密过之后的 filepassword。IV 是从 OpenSSL 中随机生成的,解密算法需要 key 和 IV。
为了保证 key rotate 的崩溃恢复,在 Keyring 中的保存的不仅仅是 master key 的密文,还有 seqno, 那么保存 seqno 的明文是什么呢 ? 有以下几种:
- MySQLReplicationKey_{UUID}
- old_MySQLReplicationKey_{UUID}
- new_MySQLReplicationKey_{UUID}
- last_purged_MySQLReplicationKey_{UUID}
举个例子,Rotate 的时候需要获得一个新的 seqno,如果出现了 crash,重启的时候如何获得老的 seqno 呢 ?因此在 rotate 的时候会先把老的 seqno 放到 old_MySQLReplicationKey_{UUID} 为明文的 keyring 中。
代码解析
核心类
Binlog_encryption_ostream 类负责写入流程,继承了 Truncatable_ostream,和之前写文件的 IO_CACHE_stream 类似, m_down_ostream 是 IO_CACHE_stream 接口,加密后写到文件中,从 m_header 中获得 file password。 具体的加密和解密工作由 m_encryptor 负责。
class Binlog_encryption_ostream : public Truncatable_ostream {
public:
private:
std::unique_ptr<Truncatable_ostream> m_down_ostream;
std::unique_ptr<Rpl_encryption_header> m_header;
std::unique_ptr<Rpl_cipher> m_encryptor;
}
这两个类负责管理 Binlog 文件头保存的信息,V1 是目前的版本,说明官方设计代码的时候考虑到了以后数据格式的变化。
class Rpl_encryption_header_v1 : public Rpl_encryption_header {
private:
/* The key ID of the keyring key that encrypted the password */
std::string m_key_id;
/* The encrypted file password */
Key_string m_encrypted_password;
/* The IV used to encrypt/decrypt the file password */
Key_string m_iv;
}
Rpl_encryption 类负责管理 master key,和 keyring 交互,包括 key rotate 和崩溃恢复, 在代码中是一个单例。
class Rpl_encryption {
/* master key id 接口*/
struct Rpl_encryption_key {
std::string m_id;
Key_string m_value;
};
}
初始化
加密是文档级别的,在打开每个 binlog 的文件会去判断 Encryption 是不是 enable 了,如果判断需要加密,就初始化 m_pipiline_head 为 Binlog_encryption_ostream.
/* 照常打开 Binlog_ofile */
bool MYSQL_BIN_LOG::Binlog_ofile::open(
const char *binlog_name, myf flags, bool existing = false)) {
/* 正常的打开 IO_CACHE_ostream */
std::unique_ptr<IO_CACHE_ostream> file_ostream(new IO_CACHE_ostream);
if (file_ostream->open(log_file_key, binlog_name, flags)) DBUG_RETURN(true);
m_pipeline_head = std::move(file_ostream);
/* Setup encryption for new files if needed */
if (!existing && rpl_encryption.is_enabled()) {
std::unique_ptr<Binlog_encryption_ostream> encrypted_ostream(
new Binlog_encryption_ostream());
/* 把刚刚打开的 IO_CACHE_ostream 放到 Binlog_encryption_ostream::down_ostream */
/* 加密完成之后会继续用 down_ostream 写到文件里 */
if (encrypted_ostream->open(std::move(m_pipeline_head)))
DBUG_RETURN(true);
m_encrypted_header_size = encrypted_ostream->get_header_size();
m_pipeline_head = std::move(encrypted_ostream);
}
}
加密
加密的入口是 Binlog_encryption_ostream::write 函数,具体加密的工作是由 Rpl_cipher::encrypt 来做的,而 Rpl_cipher 需要的加密所用的 key 是由 Rpl_encryption_header 提供的。
bool Binlog_encryption_ostream::open(
std::unique_ptr<Truncatable_ostream> down_ostream) {
DBUG_ASSERT(down_ostream != nullptr);
m_header = Rpl_encryption_header::get_new_default_header();
/* 从 header 中产生一个 random 的 filepassword,然后用 master key 加密*/
const Key_string password_str = m_header->generate_new_file_password();
/* 取出 Aes_ctr,目前的加密方式是 Aes,是一个子类的具体实现 */
m_encryptor = m_header->get_encryptor();
}·
Binlog_encryption_ostream::write 中按照 ENCRYPT_BUFFER_SIZE = 2048 的大小块加密文件,加密后写到 IO_CACHE_ostream 中。
bool Binlog_encryption_ostream::write(const unsigned char *buffer,
my_off_t length) {
/*
Split the data in 'buffer' to ENCRYPT_BUFFER_SIZE bytes chunks and
encrypt them one by one.
*/
while (length > 0) {
int encrypt_len =
std::min(length, static_cast<my_off_t>(ENCRYPT_BUFFER_SIZE));
if (m_encryptor->encrypt(encrypt_buffer, ptr, encrypt_len)) {
THROW_RPL_ENCRYPTION_FAILED_TO_ENCRYPT_ERROR;
return true;
}
if (m_down_ostream->write(encrypt_buffer, encrypt_len)) return true;
ptr += encrypt_len;
length -= encrypt_len;
}
}
解密
一个 Binlog 文件是不是加密的,是有文件头部的 magic num 决定的,当打开一个文件后,会调用函数 Basic_binlog_ifile::read_binlog_magic(),取出 magic num 后判断是否加密,以此来初始化。encryption_istream 的管理类似 Binlog_encryption_ostream,不在赘述。
bool Basic_binlog_ifile::read_binlog_magic() {
/*
If this is an encrypted stream, read encryption header and setup up
encryption stream pipeline.
*/
if (memcmp(magic, Rpl_encryption_header::ENCRYPTION_MAGIC,
Rpl_encryption_header::ENCRYPTION_MAGIC_SIZE) == 0) {
std::unique_ptr<Binlog_encryption_istream> encryption_istream{
new Binlog_encryption_istream()};
if (encryption_istream->open(std::move(m_istream), m_error))
DBUG_RETURN(true);
/* Setup encryption stream pipeline */
m_istream = std::move(encryption_istream);
/* Read binlog magic from encrypted data */
if (m_istream->read(magic, BINLOG_MAGIC_SIZE) != BINLOG_MAGIC_SIZE) {
DBUG_RETURN(m_error->set_type(Binlog_read_error::BAD_BINLOG_MAGIC));
}
}
}
MASTER KEY ROTATE
Rotate 分为几个阶段,代码上从上面的阶段可以走到下面的阶段,在 recover_master_key 的时候会直接走到对应的的阶段去。
enum class Key_rotation_step {
START,
DETERMINE_NEXT_SEQNO,
GENERATE_NEW_MASTER_KEY,
REMOVE_MASTER_KEY_INDEX,
STORE_MASTER_KEY_INDEX,
ROTATE_LOGS,
PURGE_UNUSED_ENCRYPTION_KEYS,
REMOVE_KEY_ROTATION_TAG
};
每个阶段都做什么:
- START: 把现有的 seqno 放到 keyring 中,key 是 ‘old’ 字样的开头
if (m_master_key_seqno > 0) { /* We do not store old master key seqno into Keyring if it is zero. */ if (set_old_master_key_seqno_on_keyring(m_master_key_seqno)) goto err1; } - DETERMINE_NEXT_SEQNO: 循环遍历下一个 sequno 是多少,从当前的 seqno 递增。
do { ++new_master_key_seqno; /* Check if the key already exists */ std::string candidate_key_id = Rpl_encryption_header::seqno_to_key_id(new_master_key_seqno); auto pair = get_key(candidate_key_id, Rpl_encryption_header::get_key_type()); /* If unable to check if the key already exists */ if ((pair.first != Keyring_status::KEY_NOT_FOUND && pair.first != Keyring_status::SUCCESS) || DBUG_EVALUATE_IF("fail_to_fetch_key_from_keyring", true, false)) { Rpl_encryption::report_keyring_error(pair.first); goto err1; } /* If the key already exists on keyring */ candidate_key_fetch_status = pair.first; } while (candidate_key_fetch_status != Keyring_status::KEY_NOT_FOUND); // 找到之后放到 keyring 中,加上 new 关键字。 if (set_new_master_key_seqno_on_keyring(new_master_key_seqno)) goto err1; - GENERATE_NEW_MASTER_KEY:这一步会重新获得全局 Rpl_encryption 中的 master key,用来加密后面的数据
/* Request the keyring to generate a new master key by key id "MySQLReplicationKey\_{UUID}\_{SEQNO}" using `new master key SEQNO` as SEQNO. */ if (generate_master_key_on_keyring(new_master_key_seqno)) goto err1; - REMOVE_MASTER_KEY_INDEX:把老的 seqno 移除。
/* We did not store a master key seqno into keyring if m_master_key_seqno is 0. */ if (m_master_key_seqno != 0) { if (remove_master_key_seqno_from_keyring()) goto err1; } - STORE_MASTER_KEY_INDEX : 把新的 seqno 用正常的 key (不带关键字)存起来
if (set_master_key_seqno_on_keyring(new_master_key_seqno)) goto err1; - ROTATE_LOGS:rotate binlog 和 relay log, 从后往前遍历所有文件,重新加密 filepassword
/* We do not rotate and re-encrypt logs during recovery. */ if (m_master_key_recovered && current_thd) { /* Rotate binary logs and re-encrypt previous existent binary logs. */ if (mysql_bin_log.is_open()) { if (DBUG_EVALUATE_IF("fail_to_rotate_binary_log", true, false) || mysql_bin_log.rotate_and_purge(current_thd, true)) { goto err2; } if (mysql_bin_log.reencrypt_logs()) return true; } /* Rotate relay logs and re-encrypt previous existent relay logs. */ if (flush_relay_logs_cmd(current_thd)) goto err2; if (reencrypt_relay_logs()) return true; } - PURGE_UNUSED_ENCRYPTION_KEYS : 把带 ‘last_purged’ 的关键字 keyring 的 seqno 删除。
- REMOVE_KEY_ROTATION_TAG : 把第二步带 ‘new’ 关键字的 keyring 的 seqno 删除。
总结
Binlog 加密对于数据安全性非常必要,在 8.0.17 开始使用 AES-CTR 加密 binlog temp file, 网络传输中的依然是明文,需要使用网络加密来保证。