MySQL · 内核特性 · semi-join四个执行strategy
Author: 马苗
一 semi-join介绍
所谓的semi-join就是一个子查询,它主要用于去重,当外表查找在内表满足条件的records时,返回外表的records,也就是说它只返回存在内表中的外表的记录,如下图所示: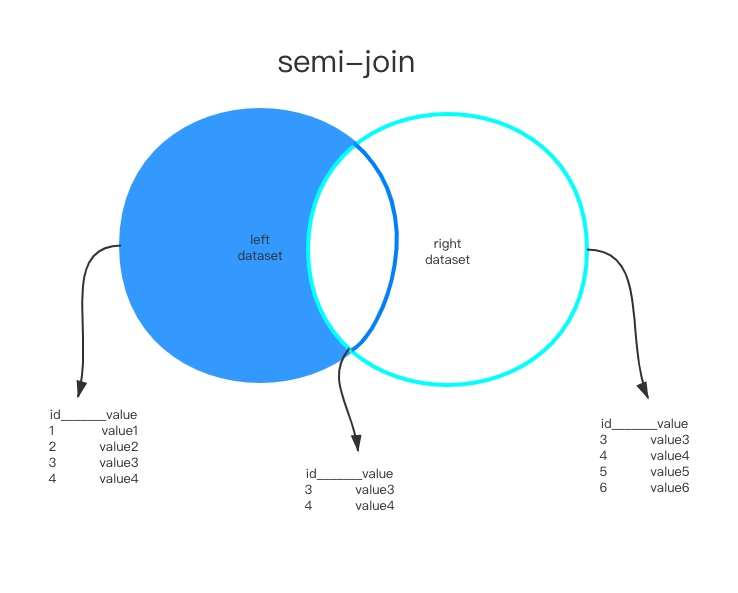
对应的语法:
SELECT ... From Outer_tables WHERE expr in (SELECT ... From Inner_tables ...) And ...
SELECT ... From Outer_tables WHERE expr exist (SELECT ... From Inner_tables ...) And ...
语法的特征
- semi-join子查询必须EXSIT和IN语句组成的布尔表达式,并且在外层查询的WHERE或者ON子句中出现。
- 外层查询也可以有其他的搜索条件,只不过和IN子查询的搜索条件必须使用AND连接起来。
- semi-join子查询必须是一个单一的查询,不能是由若干查询由UNION连接起来的形式。
- semi-join子查询不能包含GROUP BY或者HAVING语句或者聚集函数。
二 semi-join的策略
这里以mysql8.0.13为例,讲一下semi-join的几个执行策略:
DuplicateWeedout strategy
使用tmp_table, 按照join order, 选择记录qep_tab table的rowid作为唯一key进行去重,为了更好的理解,举一个例子:
SQL:
SELECT Country.Name
FROM Country
WHERE Code IN
(SELECT CountryCode
FROM City
WHERE Population > 1M)
Duplicateweedout示意图: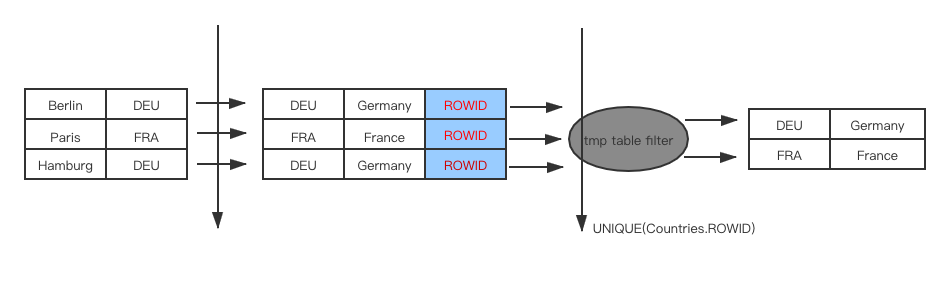
处理过程:
- 找到duplicate weedout的qep_tab range
/*找到sj的一个tab, 即第一个non-constant table*/
QEP_TAB *const first_sj_tab = qep_array + first_table;
/*这里由于last duplicate weedout table是outer join中的一个inner tables,
这里遍历找到last_sj_tab*/
if (last_sj_tab->first_inner() != NO_PLAN_IDX &&
first_sj_tab->first_inner() != last_sj_tab->first_inner()) {
QEP_TAB *tab2 = &qep_array[last_sj_tab->first_inner()];
while (tab2->first_upper() != NO_PLAN_IDX &&
tab2->first_upper() != first_sj_tab->first_inner())
tab2 = qep_array + tab2->first_upper();
if (qep_array[tab2->first_inner()].last_inner() > last_sj_tab->idx())
last_sj_tab =
&qep_array[qep_array[tab2->first_inner()].last_inner()];
}
- 记录需要记录rowid的qep_tab和jt_rowid_offset(duplicate_weedout_tmp_table的column长度)
for (QEP_TAB *tab_in_range = qep_array + first_table; tab_in_range <= last_sj_tab; tab_in_range++) { if (sj_table_is_included(join, join->best_ref[tab_in_range->idx()])) { ... jt_rowid_offset += tab_in_range->table()->file->ref_length; ... tab_in_range->keep_current_rowid = true; } } - 当发现需要记录jt_rowid_offset > 0时:
- 如果jt_rowid_offset + null_bytes为长度 > 512,就创建名为
的Field_longlong做为tmp_table的hash_field来去重 - 如果jt_rowid_offset + null_bytes为长度 <= 512,就创建名为rowids的Field_varstring作为weedout_key的tmp_table来去重
- 如果jt_rowid_offset + null_bytes为长度 > 512,就创建名为
- 执行是在do_sj_dups_weedout函数中会将需要记录rowid的qep_tab->table的h->ref(rowid存在这里)写入tmp_table中的visible_field_ptr()[0]中,在ha_write_row的时候会根据record是否与上一条record重复来决定是否写入,外层调用会对返回值判断来查看是否是需要写入的记录,从而达到去重的目的
执行计划
start temporary 和 end temporary表示duplicateweedout的qep_tab range区间

Firstmatch Strategy
只扫描外表同样结果的一条记录用于匹配内表,其好处就是避免单条记录匹配内表多条记录而产生的重复的记录,也是一种去重的方式,其示意图如下: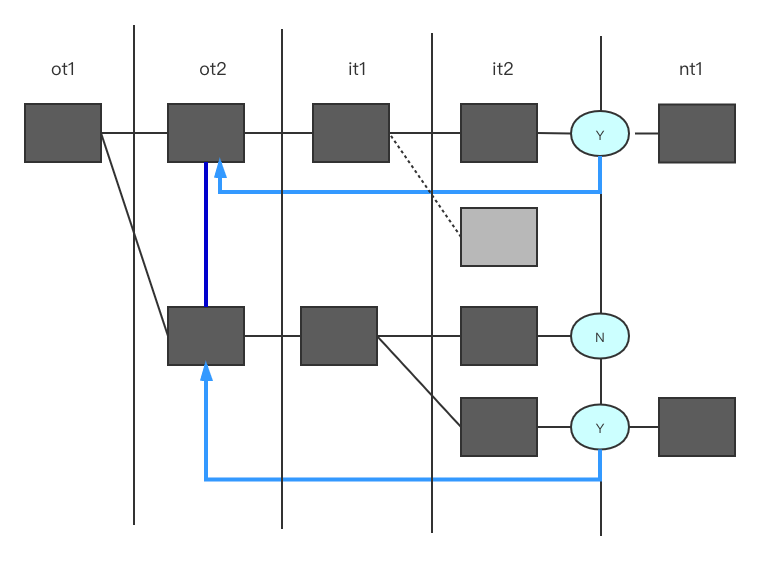
处理流程:
- 找到sj range的跳转的qep_tab和记录比较qep_tab
plan_idx jump_to = tab->idx() - 1; for (QEP_TAB *tab_in_range = tab; tab_in_range <= last_sj_tab; tab_in_range++) { if (!join->best_ref[tab_in_range->idx()]->emb_sj_nest) { jump_to = tab_in_range->idx(); } else { if (tab_in_range == last_sj_tab || !join->best_ref[tab_in_range->idx() + 1]->emb_sj_nest) { /*记录match后跳转的qep_tap*/ tab_in_range->firstmatch_return = jump_to; /*记录比较的位置*/ tab_in_range->match_tab = last_sj_tab->idx(); } } } - 执行期间匹配到满足的记录就直接跳到last outer table(ot2)
if(table condition satisfied) { do join with next tables; jump out to the jump_to; } else { discard row combination; continue current table scan; }执行计划
last semijoin table的qep_tab记录firstmatch标记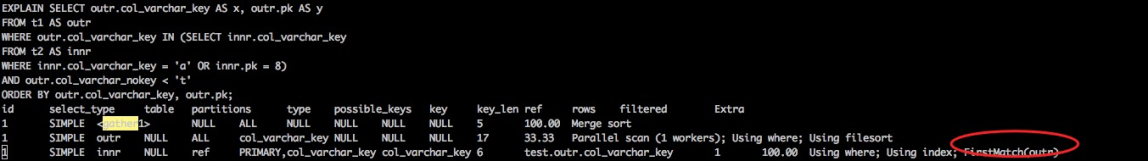
Loosescan Strategy
inner table 基于index进行分组, 分组后与outer table join, 进行condition的匹配,如果匹配到了的记录,提取outer table的记录,inner table 选取下一个分组继续进行计算。
Query:
SELECT ...
FROM ot1, ...
WHERE outer_expr IN
(SELECT it1.key
FROM it1,
it2
WHERE cond(it1, it2))
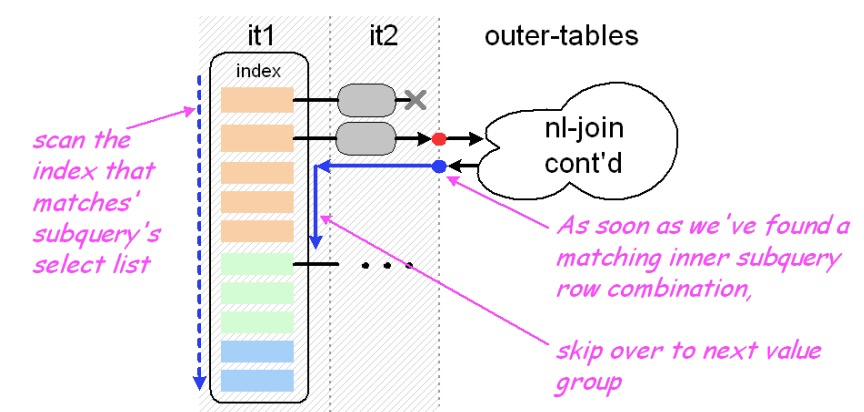
处理过程
- 选择loosescan_parts作为内表的index
- 计算 loosescan parts的长度 loosescan_key_len
- alloc loosescan_buf挂在执行loosescan的qep_tab上
- 执行过程中如果发现有匹配的记录,则key_copy copy key_info到loosescan_buf上,后续用key_cmp对loosescan_buf进行比较来做分组的过滤
执行计划
与firstmatch相同在last semijoin table的qep_tab记录looseScan标记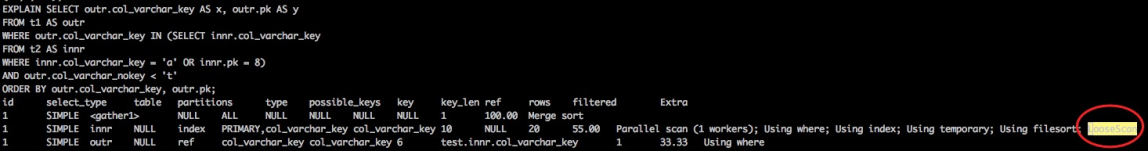 ###
###
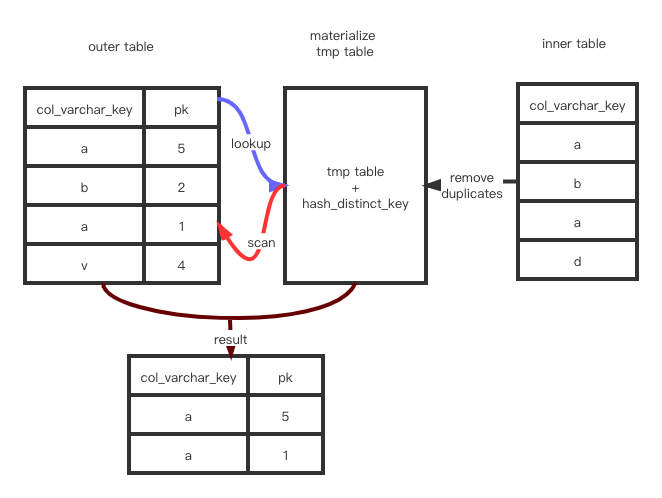
Materialize scan/Materialize lookup Strategy
将inner tables物化成temp table,通过扫描物化表或者对物化表查找的方式来避免重复record
!
处理过程
- setup_semijoin_materialized_table创建一个tmp table放在qep_tab的sjm_exec->table
- 在prepare_scan的join_materialize_semijoin(materialize钩子函数)物化semijoin nested table
/*semijoin 第一个内层物化table所在的qep_tab*/ QEP_TAB *const first = tab->join()->qep_tab + sjm->inner_table_index; /*semijoin 最后一个内层物化table所在的qep_tab*/ QEP_TAB *const last = first + (sjm->table_count - 1); last->next_select = end_sj_materialize; last->set_sj_mat_exec(sjm); // TODO: This violates comment for sj_mat_exec! if (tab->table()->hash_field) tab->table()->file->ha_index_init(0, 0); int rc; /*物化过程*/ if ((rc = sub_select(tab->join(), first, false)) < 0) DBUG_RETURN(rc); if ((rc = sub_select(tab->join(), first, true)) < 0) DBUG_RETURN(rc); if (tab->table()->hash_field) tab->table()->file->ha_index_or_rnd_end(); - end_sj_materialize 将物化结果写入sjm->table中
Materialization-scan与Materialization-lookup的区别:
- Materialization-Scan:
temporary table–> outer tabl
- Materialization-lookup
outer table–>temporary table
执行计划
MATERIALIZED代表使用了物化策略 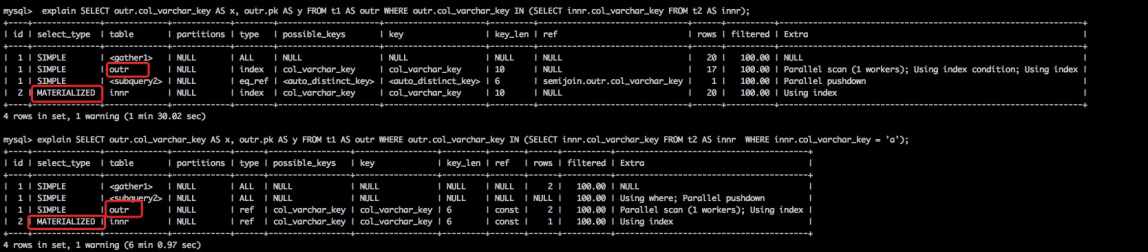
三 如何使用semi-join的策略
-
optimizer_switch
optimizer_switch 可以对semi-join使用的策略进行,其配置参数有:
semijoin : on/off
materialization : on/off
firstmatch : on/off
loosescan : on/off
duplicateweedout : on/off -
Optimizer Hints
Optimizer Hints 可以支持在SQL中hint方式指定semi-join使用的策略, 如:
指定TPCH Q20 使用duplicateweedout策略:SELECT /*+ JOIN_PREFIX(nation) */ s_name, s_address FROM supplier, nation WHERE s_suppkey IN (SELECT /*+ SEMIJOIN(DUPSWEEDOUT) */ ps_suppkey FROM partsupp WHERE ps_partkey IN (SELECT p_partkey FROM part WHERE p_name LIKE 'peru%' ) AND ps_availqty > (SELECT 0.5 * sum(l_quantity) FROM lineitem WHERE l_partkey = ps_partkey AND l_suppkey = ps_suppkey AND l_shipdate >= '1993-01-01' AND l_shipdate < date_add('1993-01-01' ,interval '1' YEAR) ) ) AND s_nationkey = n_nationkey AND n_name = 'PERU' ORDER BY s_name;
四 并行执行中的semi-join
对于选择semi-join策略的查询,PolarDB产品对semi-join所有策略实现了并行加速,根据代价评估,通过拆分semi-join的任务,多线程模型并行运行任务集,加速去重,使查询性能得到了显著的提升,以Q20为例
select
s_name,
s_address
from
supplier, nation
where
s_suppkey in (
select
ps_suppkey
from
partsupp
where
ps_partkey in (
select
p_partkey
from
part
where
p_name like '[COLOR]%'
)
and ps_availqty > (
select
0.5 * sum(l_quantity)
from
lineitem
where
l_partkey = ps_partkey
and l_suppkey = ps_suppkey
and l_shipdate >= date('[DATE]’)
and l_shipdate < date('[DATE]’) + interval ‘1’ year
)
)
and s_nationkey = n_nationkey
and n_name = '[NATION]'
order by
s_name;
我们将物化处理提前,并且达到了32个worker的并行处理能力,后续的处理通过共享之前的物化表,同样充分发挥CPU的处理能力,启动32个worker将主查询的并行能力最大化,如下图的执行计划所示,在数据量1S,开启并行后,双重并行处理能力: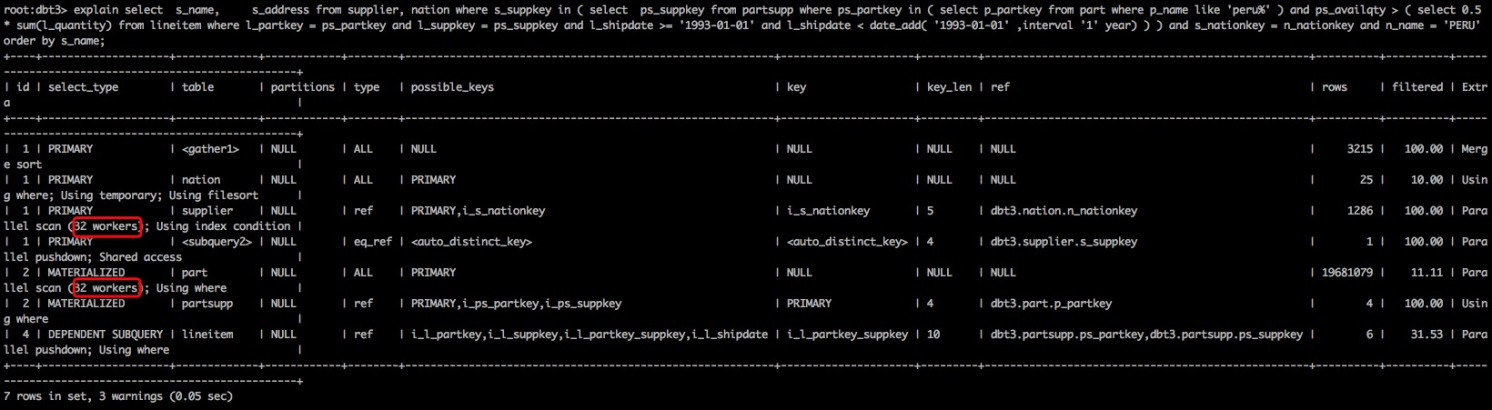
在1s数据情况下,串行的执行时间:
并行开启情况下的执行时间:
以如下自定义SQL为例, 该SQL并行使用了semi-join下推的并行方式,在max_parallel_degree=32的情况下,并行使用32个worker执行,执行时间从2.59s减少到0.34s:
mysql> SELECT c1,d1 FROM t1 WHERE c1 IN ( SELECT t2.c1 FROM t2 WHERE t2.c1 = 'f' OR t2.c2 < 'y' ) and t1.c1 and d1 > '1900-1-1' like "R1%" ORDER BY t1.c1 DESC, t1.d1 DESC;
Empty set, 1024 warnings (0.34 sec)
mysql> set max_parallel_degree=0;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> SELECT c1,d1 FROM t1 WHERE c1 IN ( SELECT t2.c1 FROM t2 WHERE t2.c1 = 'f' OR t2.c2 < 'y' ) and t1.c1 and d1 > '1900-1-1' like "R1%" ORDER BY t1.c1 DESC, t1.d1 DESC;
Empty set, 65535 warnings (2.69 sec)
mysql> explain SELECT c1,d1 FROM t1 WHERE c1 IN ( SELECT t2.c1 FROM t2 WHERE t2.c1 = 'f' OR t2.c2 < 'y' ) and t1.c1 and d1 > '1900-1-1' like "R1%" ORDER BY t1.c1 DESC, t1.d1 DESC;
+----+--------------+-------------+------------+--------+---------------+------------+---------+----------+--------+----------+---------------------------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+--------------+-------------+------------+--------+---------------+------------+---------+----------+--------+----------+---------------------------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | <gather1> | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 33464 | 100.00 | Merge sort |
| 1 | SIMPLE | t1 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 62802 | 30.00 | Parallel scan (32 workers); Using where; Using filesort |
| 1 | SIMPLE | <subquery2> | NULL | eq_ref | <auto_key> | <auto_key> | 103 | sj.t1.c1 | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 2 | MATERIALIZED | t2 | p0,p1 | ALL | c1,c2 | NULL | NULL | NULL | 100401 | 33.33 | Using where |
+----+--------------+-------------+------------+--------+---------------+------------+------