FTS 源码阅读
Author: 孙靖渊(劲川)
官方文档
简介
FTS 是倒排索引,对索引列上的文本分词并建立 词 -> 行 + 位置 的映射。词 -> 行 通过一个额外的隐藏列 FTS_DOC_ID 和 FTS_DOC_ID_INDEX 索引完成。doc_id 是这一行的唯一标识,类似于自增唯一索引,并且在 FTS 文本更新时也会触发产生新的 doc_id。
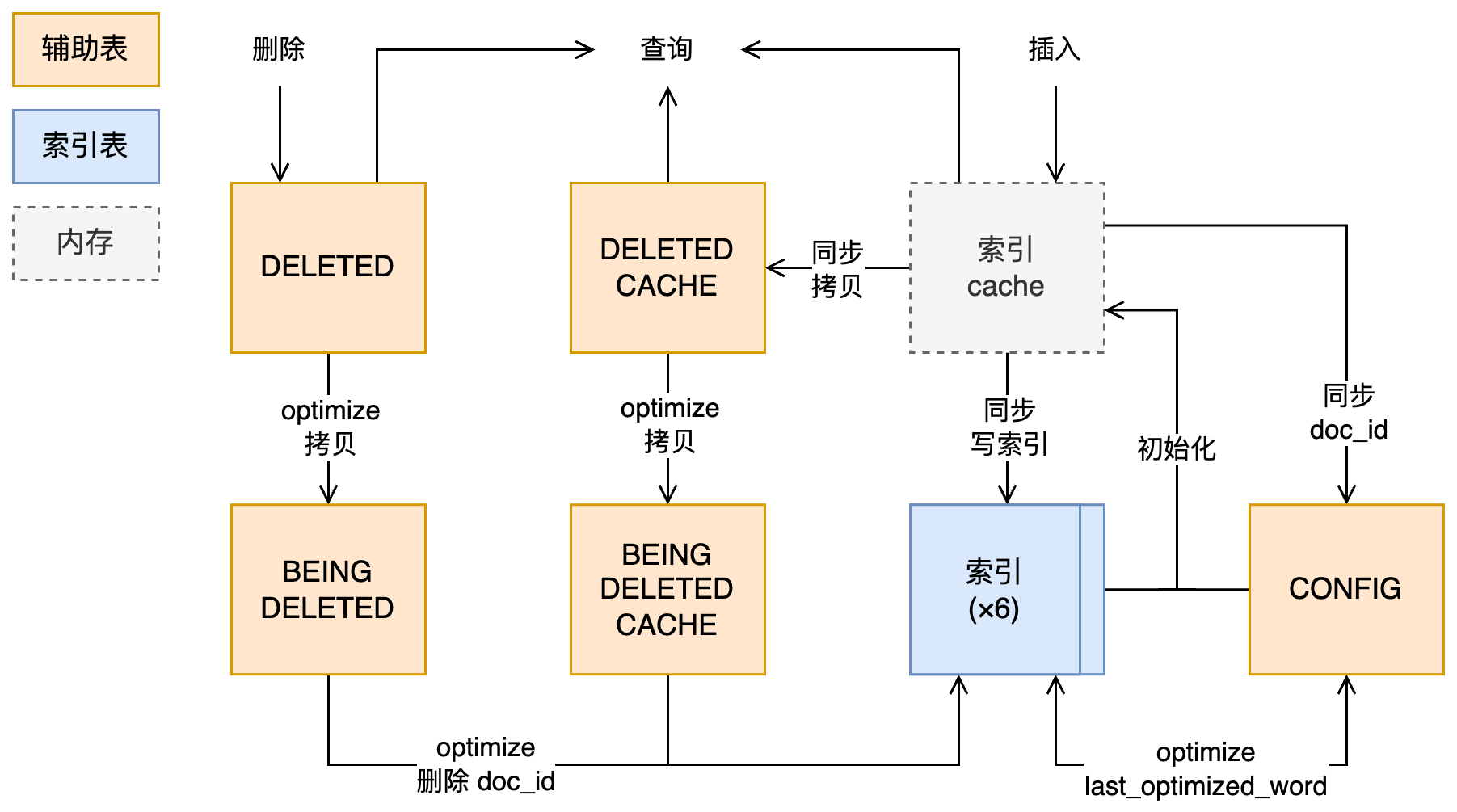
FTS 需要为每个建立 FTS 索引的表和每个 FTS 索引维护多张额外的表。这些表的维护穿插在常规建表/插入/删除等逻辑中。
FTS 的数据可见性和提交逻辑与常规数据不同:
- 即使在同一个事务内,FTS 索引的修改仅在提交后可见
- 新增文本的 FTS 索引不随事务提交而落盘,只写入内存 cache,有额外的同步操作触发落盘
- 删除文本的不删除 FTS 索引,仅记录删除的行(落盘),在 optimize 时触发真正的删除
- 由于内存 cache 的机制,RW 上的修改在 RO 上不可见,PolarDB 新增日志类型同步 FTS cache 的修改,保证 RO 的一致性
FTS 中一些重要结构和辅助表之间的关系
代码
建表
建辅助表
create_table_info_t::create_table
/* Create the ancillary tables that are common to all FTS indexes on
this table. */
if (m_flags2 & (DICT_TF2_FTS | DICT_TF2_FTS_ADD_DOC_ID)) {
fts_doc_id_index_enum ret;
/* Check whether there already exists FTS_DOC_ID_INDEX */
ret = innobase_fts_check_doc_id_index_in_def(m_form->s->keys,
m_form->key_info);
switch (ret) {
// ...
}
dberr_t err = fts_create_common_tables(m_trx, m_table, m_table_name,
(ret == FTS_EXIST_DOC_ID_INDEX));
// ...
}
innobase_fts_check_doc_id_index_in_def
检查 FTS_DOC_ID_INDEX 索引是否存在。FTS 依赖 FTS_DOC_ID 隐藏列,类型是 BIGINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL,并在列上添加唯一索引 FTS_DOC_ID_INDEX。列和索引都可以在建表时由用户显式创建,如果显示创建,用户需要自行管理 doc_id,doc_id 必须递增且不重复。
fts_create_common_tables
dberr_t fts_create_common_tables(trx_t *trx, const dict_table_t *table,
const char *name, bool skip_doc_id_index) {
// ...
FTS_INIT_FTS_TABLE(&fts_table, NULL, FTS_COMMON_TABLE, table);
/* Create the FTS tables that are common to an FTS index. */
for (ulint i = 0; fts_common_tables[i] != NULL; ++i) {
fts_table.suffix = fts_common_tables[i];
fts_get_table_name(&fts_table, full_name[i]);
dict_table_t *common_table = fts_create_one_common_table(
trx, table, full_name[i], fts_table.suffix, heap);
// ...
}
/* Write the default settings to the config table. */
error = fts_init_config_table(&fts_table);
// ...
// 建 FTS_DOC_ID_INDEX 索引
index = dict_mem_index_create(name, FTS_DOC_ID_INDEX_NAME, table->space,
DICT_UNIQUE, 1);
index->add_field(FTS_DOC_ID_COL_NAME, 0, true);
op = trx_get_dict_operation(trx);
error = row_create_index_for_mysql(index, trx, NULL, NULL);
}
建 FTS 辅助表,下列五个表由同一个表上的所有 FTS 索引共用。前四个表都是 (doc_id BIGINT UNSIGNED, UNIQUE CLUSTERED INDEX on doc_id),即记录对应 DOC_ID 行被删除的情况。这些表可以通过设置全局变量 innodb_ft_aux_table后查询 INFORMATION_SCHEMA.INNODB_FT_XXX`表访问。
- FTS_
_DELETED:已删除,但还没从 FTS 索引中删除的 docid - FTS_
_DELETED_CACHE:上表的内存中版本 - FTS_
_BEING_DELETED:正在从 FTS 索引中删除的 doc_id - FTS_
_BEING_DELETED_CACHE:上表的内存中版本 - FTS_
_CONFIG:FTS 相关配置
MySQL [(none)]> set global innodb_ft_aux_table="fts_test/fts1";
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
MySQL [(none)]> select * from information_schema.innodb_ft_config;
+---------------------------+-------+
| KEY | VALUE |
+---------------------------+-------+
| optimize_checkpoint_limit | 180 | -- 每次 optimize table 删除/合并的词数量
| synced_doc_id | 0 | -- 已经刷盘的 doc_id
| stopword_table_name | | -- stopword 表名
| use_stopword | 1 | -- 是否使用 stopword
+---------------------------+-------+
fts_create_one_common_table 按照 dd 信息创建表。fts_init_config_table写配置信息。如果不存在 FTS_DOC_ID_INDEX 则添加索引
- 建 FTS 索引表
create_index->row_create_index_for_mysql->fts_create_index_tables_low->fts_create_one_index_table
每个 FTS 索引创建 FTS_NUM_AUX_INDEX = 6 个倒排索引表,分别是 FTS_
MySQL [(none)]> select * from information_schema.innodb_ft_index_table limit 10;
+--------+--------------+-------------+-----------+--------+----------+
| WORD | FIRST_DOC_ID | LAST_DOC_ID | DOC_COUNT | DOC_ID | POSITION |
+--------+--------------+-------------+-----------+--------+----------+
| across | 3 | 14779 | 1848 | 3 | 18 |
| across | 3 | 14779 | 1848 | 11 | 18 |
| across | 3 | 14779 | 1848 | 19 | 18 |
| across | 3 | 14779 | 1848 | 27 | 18 |
| across | 3 | 14779 | 1848 | 35 | 18 |
| across | 3 | 14779 | 1848 | 43 | 18 |
| across | 3 | 14779 | 1848 | 51 | 18 |
| across | 3 | 14779 | 1848 | 59 | 18 |
| across | 3 | 14779 | 1848 | 67 | 18 |
| across | 3 | 14779 | 1848 | 75 | 18 |
+--------+--------------+-------------+-----------+--------+----------+
10 rows in set (0.04 sec)
- 记录上述所有表
dict_table_get_all_fts_indexes
/* Cache all the FTS indexes on this table in the FTS specific
structure. They are used for FTS indexed column update handling. */
if (m_flags2 & DICT_TF2_FTS) {
fts_t *fts = m_table->fts;
ut_a(fts != NULL);
dict_table_get_all_fts_indexes(m_table, fts->indexes);
}
加入 dd
create_table_info_t::create_table_update_global_dd
if (m_flags2 & (DICT_TF2_FTS | DICT_TF2_FTS_ADD_DOC_ID)) {
ut_d(bool ret =) fts_create_common_dd_tables(m_table);
ut_ad(ret);
fts_create_index_dd_tables(m_table);
}
fts_create_common_dd_tables->dd_create_fts_common_tablefts_create_index_dd_tables->fts_create_one_index_dd_tables->dd_create_fts_index_table
更新 stopword
create_table_info_t::create_table_update_dict
if (m_table->fts != NULL) {
if (m_table->fts_doc_id_index == NULL) {
m_table->fts_doc_id_index =
dict_table_get_index_on_name(m_table, FTS_DOC_ID_INDEX_NAME);
DBUG_ASSERT(m_table->fts_doc_id_index != NULL);
} else {
DBUG_ASSERT(m_table->fts_doc_id_index ==
dict_table_get_index_on_name(m_table, FTS_DOC_ID_INDEX_NAME));
}
}
/* Load server stopword into FTS cache */
if (m_flags2 & DICT_TF2_FTS) {
if (!innobase_fts_load_stopword(m_table, NULL, m_thd)) {
return -1;
}
}
加载 stopword 列表,并把表名写入 config 表。stopword 表中的词不会被加入 FTS 索引。设置全局变量innodb_ft_aux_table后查询 IS 的 INNODB_FT_DEFAULT_STOPWORD 表获得对应 FTS 的全部 stopword。默认的 stopword 列表包含了常见但没有意义的短单词,定义在
/** InnoDB default stopword list:
There are different versions of stopwords, the stop words listed
below comes from "Google Stopword" list. Reference:
http://meta.wikimedia.org/wiki/Stop_word_list/google_stop_word_list.
The final version of InnoDB default stopword list is still pending
for decision */
const char *fts_default_stopword[] = {
"a", "about", "an", "are", "as", "at", "be", "by",
"com", "de", "en", "for", "from", "how", "i", "in",
"is", "it", "la", "of", "on", "or", "that", "the",
"this", "to", "was", "what", "when", "where", "who", "will",
"with", "und", "the", "www", NULL};
stopword 表可以自由指定。建 FTS 索引之前,设置变量innodb_ft_user_stopword_table指定需要使用的 stopword 表。
innobase_fts_load_stopword` -> `fts_load_stopword` -> `fts_load_user_stopword`-> `fts_read_stopword
if (stopword_to_use && fts_load_user_stopword(table->fts, stopword_to_use,
&cache->stopword_info)) {
/* Save the stopword table name to the configure
table */
if (!reload) {
str.f_n_char = 0;
str.f_str = (byte *)stopword_to_use;
str.f_len = ut_strlen(stopword_to_use);
error =
fts_config_set_value(trx, &fts_table, FTS_STOPWORD_TABLE_NAME, &str);
}
} else {
/* Load system default stopword list */
fts_load_default_stopword(&cache->stopword_info);
}
内存中的 stopword 组织成红黑树
插入
准备
row_insert_for_mysql` -> `row_insert_for_mysql_using_ins_graph` -> `row_mysql_convert_row_to_innobase` -> `fts_create_doc_id
/** Create a new document id.
@return DB_SUCCESS if all went well else error */
dberr_t fts_create_doc_id(dict_table_t *table, /*!< in: row is of this table. */
dtuple_t *row, /* in/out: add doc id value to this
row. This is the current row that is
being inserted. */
mem_heap_t *heap) /*!< in: heap */
{
doc_id_t doc_id;
dberr_t error = DB_SUCCESS;
ut_a(table->fts->doc_col != ULINT_UNDEFINED);
// 用户定义了 doc_id 列, doc_id 由用户提供
if (!DICT_TF2_FLAG_IS_SET(table, DICT_TF2_FTS_HAS_DOC_ID)) {
if (table->fts->cache->first_doc_id == FTS_NULL_DOC_ID) {
error = fts_get_next_doc_id(table, &doc_id);
}
return (error);
}
error = fts_get_next_doc_id(table, &doc_id);
if (error == DB_SUCCESS) {
dfield_t *dfield;
doc_id_t *write_doc_id;
ut_a(doc_id > 0);
dfield = dtuple_get_nth_field(row, table->fts->doc_col);
write_doc_id =
static_cast<doc_id_t *>(mem_heap_alloc(heap, sizeof(*write_doc_id)));
ut_a(doc_id != FTS_NULL_DOC_ID);
ut_a(sizeof(doc_id) == dfield->type.len);
fts_write_doc_id((byte *)write_doc_id, doc_id);
dfield_set_data(dfield, write_doc_id, sizeof(*write_doc_id));
}
return (error);
}
插入时 FTS 需要给新的行分配 doc_id。
fts_get_next_doc_id
/* If the Doc ID system has not yet been initialized, we
will consult the CONFIG table and user table to re-establish
the initial value of the Doc ID */
if (cache->first_doc_id == FTS_NULL_DOC_ID) {
fts_init_doc_id(table);
}
fts_init_doc_id
/* Return if the table is already initialized for DOC ID */
if (table->fts->cache->first_doc_id != FTS_NULL_DOC_ID) {
rw_lock_x_unlock(&table->fts->cache->lock);
return (0);
}
DEBUG_SYNC_C("fts_initialize_doc_id");
/* Then compare this value with the ID value stored in the CONFIG
table. The larger one will be our new initial Doc ID */
fts_cmp_set_sync_doc_id(table, 0, FALSE, &max_doc_id);
/* If DICT_TF2_FTS_ADD_DOC_ID is set, we are in the process of
creating index (and add doc id column. No need to recovery
documents */
if (!DICT_TF2_FLAG_IS_SET(table, DICT_TF2_FTS_ADD_DOC_ID)) {
fts_init_index((dict_table_t *)table, TRUE);
}
启动后首次插入索引需要初始化 doc_id。
fts_cmp_set_sync_doc_id开启事务访问 config 表,比较并更新 sync_doc_id 值fts_init_index同步内存状态和数据状态,sync_doc_id 把分词信息加入内存 cache
插入
row_insert_for_mysql_using_ins_graph`-> `fts_trx_add_op`, `fts_add_doc_from_tuple
常规表 fts_trx_add_op -> fts_trx_table_add_op
FTS 的修改只在提交时可见,事务过程中的修改先添加到事务的内存结构中,并且按行记录语句级别的变更和当前保存点之后的变更。
/** Information about changed rows in a transaction for a single table. */
struct fts_trx_table_t {
dict_table_t *table; /*!< table */
fts_trx_t *fts_trx; /*!< link to parent */
ib_rbt_t *rows; /*!< rows changed; indexed by doc-id,
cells are fts_trx_row_t* */
fts_doc_ids_t *added_doc_ids; /*!< list of added doc ids (NULL until
the first addition) */
/*!< for adding doc ids */
que_t *docs_added_graph;
};
/** Information about one changed row in a transaction. */
struct fts_trx_row_t {
doc_id_t doc_id; /*!< Id of the ins/upd/del document */
fts_row_state state; /*!< state of the row */
ib_vector_t *fts_indexes; /*!< The indexes that are affected */
};
分区表修改分区过程中,中间状态的表使用fts_add_doc_from_tuple直接开 mtr 记录所有修改
提交
trx_commit_low` -> `fts_commit` -> `fts_commit_table` -> `fts_add` -> `fts_add_doc_by_id
- 根据记录的 doc_id 找到表中对应行
/* Search based on Doc ID. Here, we'll need to consider the case
when there is no primary index on Doc ID */
// ...
btr_pcur_open_with_no_init(fts_id_index, tuple, PAGE_CUR_LE, BTR_SEARCH_LEAF,
&pcur, 0, &mtr);
/* If we have a match, add the data to doc structure */
if (btr_pcur_get_low_match(&pcur) == 1) {
// ...
rec = btr_pcur_get_rec(&pcur);
/* Doc could be deleted */
if (page_rec_is_infimum(rec) ||
rec_get_deleted_flag(rec, dict_table_is_comp(table))) {
goto func_exit;
}
// FTS_DOC_ID 列也可以是主键
if (is_id_cluster) {
clust_rec = rec;
doc_pcur = &pcur;
} else {
// ...
// 回表
row_build_row_ref_in_tuple(clust_ref, rec, fts_id_index, NULL, NULL,
&heap);
btr_pcur_open_with_no_init(clust_index, clust_ref, PAGE_CUR_LE,
BTR_SEARCH_LEAF, &clust_pcur, 0, &mtr);
doc_pcur = &clust_pcur;
clust_rec = btr_pcur_get_rec(&clust_pcur);
}
offsets =
rec_get_offsets(clust_rec, clust_index, NULL, ULINT_UNDEFINED, &heap);
- 拿到文本并分词
fts_fetch_doc_from_rec->fts_tokenize_document->fts_process_token->innodb_mysql_fts_get_token(默认的内置分词) - 分词加入 FTS cache
fts_cache_add_doc
for (node = rbt_first(tokens); node; node = rbt_first(tokens)) {
// ...
/* Find and/or add token to the cache. */
// 在红黑树搜索,同时对比事先加载到 cache 的 stopword 列表
word = fts_tokenizer_word_get(cache, index_cache, &token->text);
// ...
if (ib_vector_size(word->nodes) > 0) {
fts_node = static_cast<fts_node_t *>(ib_vector_last(word->nodes));
}
// ...
fts_cache_node_add_positions(cache, fts_node, doc_id, token->positions);
ut_free(rbt_remove_node(tokens, node));
}
内存中索引的一行用 fts_node_t 表示
struct fts_node_t {
doc_id_t first_doc_id; /*!< First document id in ilist. */
doc_id_t last_doc_id; /*!< Last document id in ilist. */
byte *ilist; /*!< Binary list of documents & word
positions the token appears in.
... */
ulint doc_count; /*!< Number of doc ids in ilist */
ulint ilist_size; /*!< Used size of ilist in bytes. */
ulint ilist_size_alloc;
/*!< Allocated size of ilist in
bytes */
bool synced; /*!< flag whether the node is synced */
};
ilist(在索引中是 blob 类型)记录了分词所在的 doc_id 和对应行上的位置。doc_id 和位置都分别使用增量编码、变长编码,每一个 doc_id 后接多个位置,位置以 0 结尾。例如
12 2 1 5 0 5 30 0
│ │ │ │ │ │ │ ╰ 终止符
│ │ │ │ │ │ ╰ 第一个位置 30
│ │ │ │ │ ╰ 第二个 doc_id 12 + 5 = 17
│ │ │ │ ╰ 终止符
│ │ │ ╰ 第三个位置 3 + 5 = 8
│ │ ╰ 第二个位置 2 + 1 = 3
│ ╰ 第一个位置 2
╰ 第一个 doc_id 12
- 符合条件时分词刷到 FTS 索引
if ((cache->total_size > fts_max_cache_size / 10 || fts_need_sync) &&
!cache->sync->in_progress) {
need_sync = true;
}
// ...
if (need_sync) {
fts_optimize_request_sync_table(table);
}
清理
trx_commit_in_memory -> trx_finalize_for_fts -> trx_finalize_for_fts_table,清理阶段实际上什么都没有做
/********************************************************************
Finalize a transaction containing updates for a FTS table. */
static void trx_finalize_for_fts_table(
fts_trx_table_t *ftt) /* in: FTS trx table */
{
fts_t *fts = ftt->table->fts;
fts_doc_ids_t *doc_ids = ftt->added_doc_ids;
mutex_enter(&fts->bg_threads_mutex);
if (fts->fts_status & BG_THREAD_STOP) {
/* The table is about to be dropped, no use
adding anything to its work queue. */
mutex_exit(&fts->bg_threads_mutex);
} else {
mem_heap_t *heap;
mutex_exit(&fts->bg_threads_mutex);
ut_a(fts->add_wq);
heap = static_cast<mem_heap_t *>(doc_ids->self_heap->arg);
ib_wqueue_add(fts->add_wq, doc_ids, heap);
/* fts_trx_table_t no longer owns the list. */
ftt->added_doc_ids = NULL;
}
}
代码里面提到了fts->add_wq和BG_THREAD_STOP,暗示原来有/有计划增加更多的后台线程,在 FTS 相关事务 commit 之后触发同步或 optimize 逻辑。fts_t中也有相关引用。
/** The state of the FTS sub system. */
class fts_t {
public:
// ...
/** Number of background threads accessing this table. */
// 没有用
ulint bg_threads;
/** Status bit regarding fts running state. TRUE if background
threads running should stop themselves. */
ulint fts_status;
// 没有用
ib_wqueue_t *add_wq;
// ...
};
下面的前三个 status 在代码中没有用。
enum fts_status {
BG_THREAD_STOP = 1, /*!< TRUE if the FTS background thread
has finished reading the ADDED table,
meaning more items can be added to
the table. */
BG_THREAD_READY = 2, /*!< TRUE if the FTS background thread
is ready */
ADD_THREAD_STARTED = 4, /*!< TRUE if the FTS add thread
has started */
ADDED_TABLE_SYNCED = 8, /*!< TRUE if the ADDED table record is
sync-ed after crash recovery */
};
安全性
由于 FTS 索引的内容本质上是冗余的,如果内存 cache 丢失(比如db crash)只需要重新从索引列上的文本产生即可。每次同步时,CONFIG 表中记录了同步到的 syncdocid。初始化一个表上的 FTS 索引时,只需要从这个 docid 开始重新加载 FTS cache 即可。
fts_init_index` -> `fts_doc_fetch_by_doc_id`(`FTS_FETCH_DOC_BY_ID_LARGE`模式)-> `fts_init_recover_doc
常规情况下,只要插入记录的事务提交,FTS 索引内容可以恢复。
删除
删除
先准备 FK 相关表的 doc_id row_update_for_mysql_using_upd_graph-> init_fts_doc_id_for_ref->fts_init_doc_id,然后记录插入操作 row_fts_update_or_delete->fts_trx_add_op->fts_trx_table_add_op。删除和插入的过程类似,事务过程中只把删除操作记录在内存中。
提交
trx_commit_low` -> `fts_commit` -> `fts_commit_table` -> `fts_delete
FTS 的删除并不从 FTS 索引中删除对应的记录,而是将删除的 doc_id 记录在 FTS_
/* It is possible we update a record that has not yet been sync-ed
into cache from last crash (delete Doc will not initialize the
sync). Avoid any added counter accounting until the FTS cache
is re-established and sync-ed */
if (table->fts->fts_status & ADDED_TABLE_SYNCED &&
doc_id > cache->synced_doc_id) {
mutex_enter(&table->fts->cache->deleted_lock);
/* The Doc ID could belong to those left in
ADDED table from last crash. So need to check
if it is less than first_doc_id when we initialize
the Doc ID system after reboot */
if (doc_id >= table->fts->cache->first_doc_id &&
table->fts->cache->added > 0) {
--table->fts->cache->added;
}
mutex_exit(&table->fts->cache->deleted_lock);
/* Only if the row was really deleted. */
ut_a(row->state == FTS_DELETE || row->state == FTS_MODIFY);
}
/* Note the deleted document for OPTIMIZE to purge. */
if (error == DB_SUCCESS) {
// ...
fts_table.suffix = FTS_SUFFIX_DELETED;
fts_get_table_name(&fts_table, table_name);
pars_info_bind_id(info, true, "deleted", table_name);
graph = fts_parse_sql(&fts_table, info,
"BEGIN INSERT INTO $deleted VALUES (:doc_id);");
error = fts_eval_sql(trx, graph);
fts_que_graph_free(graph);
} else {
pars_info_free(info);
}
/* Increment the total deleted count, this is used to calculate the
number of documents indexed. */
// ...
原子性问题
提交过程先提交 DELETED 表修改,然后提交事务。在这两个步骤之间 crash,会导致 DELETED 表包含了没有删除的 doc_id,这行会无法通过 FTS 搜索到。
/* undo_no is non-zero if we're doing the final commit. */
if (trx->fts_trx != NULL && trx->undo_no != 0 &&
trx->lock.que_state != TRX_QUE_ROLLING_BACK) {
dberr_t error;
ut_a(!trx_is_autocommit_non_locking(trx));
error = fts_commit(trx);
/* FTS-FIXME: Temporarily tolerate DB_DUPLICATE_KEY
instead of dying. This is a possible scenario if there
is a crash between insert to DELETED table committing
and transaction committing. The fix would be able to
return error from this function */
if (error != DB_SUCCESS && error != DB_DUPLICATE_KEY) {
/* FTS-FIXME: once we can return values from this
function, we should do so and signal an error
instead of just dying. */
ut_error;
}
DBUG_INJECT_CRASH("after_fts_commit_before_trx_commit", 1); // <-- crash
}
理论上,只要在用户的事务中操作 DELETED 表就可以保证 FTS 的操作和表的操作原子,但是按照
When processing deleted record at the transaction commit time, do not · mysql/mysql-server@d1a7634
此时用户事务已经处于 prepared 阶段。
更新
首先确认更新和 FTS 有关ha_innodb::update_row -> calc_row_difference。FTS 把更新处理为删除+插入,索引覆盖的列和 doc_id 列有任意修改就做在 FTS 索引上做一次完整的删除和插入。
if (prebuilt->table->fts != NULL && !is_virtual) {
ulint offset;
dict_table_t *innodb_table;
innodb_table = prebuilt->table;
if (!changes_fts_column) {
offset = row_upd_changes_fts_column(innodb_table, ufield);
if (offset != ULINT_UNDEFINED) {
changes_fts_column = TRUE;
}
}
if (!changes_fts_doc_col) {
changes_fts_doc_col = row_upd_changes_doc_id(innodb_table, ufield);
}
}
潜在优化:一个表上可能有多个 FTS 索引,一个索引可能覆盖多个列。目前的实现中任意 FTS 相关更新会更新全部 FTS 索引,但是有针对选择性更新的设计。
/* If an FTS indexed column was changed by this
UPDATE then we need to inform the FTS sub-system.
NOTE: Currently we re-index all FTS indexed columns
even if only a subset of the FTS indexed columns
have been updated. That is the reason we are
checking only once here. Later we will need to
note which columns have been updated and do
selective processing. */
doc_id 如果由用户管理,需要满足更新规则:
- 如果 FTS 索引覆盖的列有更新,doc_id 也需要更新
- doc_id 必须严格单调增
- doc_id 的增量不能太大(
>= FTS_DOC_ID_MAX_STEP) ,这个限制可能是由于 docid 按照增量储存在 ilist 内
如果是隐藏列则 FTS 会自动生成一个新的 doc_id
if () {
// 如果没有 FTS
} else if (changes_fts_column || changes_fts_doc_col) {
dict_table_t *innodb_table = prebuilt->table;
ufield = uvect->fields + n_changed;
if (!DICT_TF2_FLAG_IS_SET(innodb_table, DICT_TF2_FTS_HAS_DOC_ID)) {
// 检查 doc_id
// ...
trx->fts_next_doc_id = doc_id;
} else {
/* If the Doc ID is a hidden column, it can't be
changed by user */
ut_ad(!changes_fts_doc_col);
/* Doc ID column is hidden, a new Doc ID will be
generated by following fts_update_doc_id() call */
trx->fts_next_doc_id = 0;
}
fts_update_doc_id(innodb_table, ufield, &trx->fts_next_doc_id);
++n_changed;
} else {
/* We have a Doc ID column, but none of FTS indexed
columns are touched, nor the Doc ID column, so set
fts_next_doc_id to UINT64_UNDEFINED, which means do not
update the Doc ID column */
trx->fts_next_doc_id = UINT64_UNDEFINED;
}
确认有更新后,
row_fts_update_or_delete -> row_fts_do_update,向事务添加删除和插入操作
/********************************************************************
Handle an update of a column that has an FTS index. */
static void row_fts_do_update(
trx_t *trx, /* in: transaction */
dict_table_t *table, /* in: Table with FTS index */
doc_id_t old_doc_id, /* in: old document id */
doc_id_t new_doc_id) /* in: new document id */
{
if (trx->fts_next_doc_id) {
fts_trx_add_op(trx, table, old_doc_id, FTS_DELETE, NULL);
if (new_doc_id != FTS_NULL_DOC_ID) {
fts_trx_add_op(trx, table, new_doc_id, FTS_INSERT, NULL);
}
}
}
同步
通常在修改 FTS 索引时,修改不会直接写入索引(FTS_
- 用户执行
OPTIMIZE TABLE,并且innodb_optimize_fulltext_only = ON则只优化 FTS 索引 - insert 提交时,单表索引 cache 大小超过
fts_max_cache_size / 10,调用fts_optimize_request_sync_table提交同步任务给后台线程fts_optimize_thread - 修改分区表过程中,FTS 的插入都是直接进入索引 cache 的,单表索引 cache 大小超过
fts_max_cache_size / 5直接触发同步fts_sync - inplace
ALTER TABLE,调用row_merge_read_clustered_index->fts_sync_table - 后台线程也定期检查 FTS 索引 cache 总大小,如果超过
fts_max_total_cache_size就设置fts_need_sync并在下次插入 cache 时(即2、3两个场景)触发同步。 - 数据库正常关闭
常规同步的路径 fts_optimize_thread -> fts_optimize_sync_table -> fts_sync_table -> fts_sync -> fts_sync_index -> fts_sync_write_words
选择索引表
/* We iterate over the entire tree, even if there is an error,
since we want to free the memory used during caching. */
for (rbt_node = rbt_first(index_cache->words); rbt_node;
rbt_node = rbt_next(index_cache->words, rbt_node)) {
// ...
selected = fts_select_index(index_cache->charset, word->text.f_str,
word->text.f_len);
fts_table.suffix = fts_get_suffix(selected);
索引共有 6 个表,在非 CJK 字符集下按照第一个字符(的第一个字节)分片:
/** FTS auxiliary INDEX split intervals. */
const fts_index_selector_t fts_index_selector[] = {
{9, "index_1"}, {65, "index_2"}, {70, "index_3"}, {75, "index_4"},
{80, "index_5"}, {85, "index_6"}, {0, NULL}};
对应 ASCII 字符,差不多把大写字母平均划分
| 9 | 65 | 70 | 75 | 80 | 85 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TAB | A | F | K | P | U |
(按照代码,fts_index_selector[0]没有实际用处)
UNIV_INLINE
ulint fts_select_index_by_range(const CHARSET_INFO *cs, const byte *str,
ulint len) {
ulint selected = 0;
ulint value = innobase_strnxfrm(cs, str, len);
while (fts_index_selector[selected].value != 0) {
if (fts_index_selector[selected].value == value) {
return (selected);
} else if (fts_index_selector[selected].value > value) {
return (selected > 0 ? selected - 1 : 0);
}
++selected;
}
ut_ad(selected > 1);
return (selected - 1);
}
写入索引
写入的时候可以选择是否释放表上 cache 的锁,后台线程同步时选择放锁。为了避免正在同步的 node 被修改需要设置 fts_node->synced,写入 cache 时会检查这个标记。
if (fts_node->synced) {
continue;
} else {
fts_node->synced = true;
}
/*FIXME: we need to handle the error properly. */
if (error == DB_SUCCESS) {
// ...
if (unlock_cache) {
rw_lock_x_unlock(&table->fts->cache->lock);
}
error = fts_write_node(trx, &index_cache->ins_graph[selected],
&fts_table, &word->text, fts_node);
// ...
if (unlock_cache) {
rw_lock_x_lock(&table->fts->cache->lock);
}
DDL 过程中一般始终持有这个锁。由于这个锁可能长期持有(cache 特别大时手动触发OPTIMIZE TABLE)超过 innodb mutex 持有时间上限,这里有临时延长 mutex 持有上限的逻辑,并且在极端情况下也会放锁。
由于写索引的过程中可能放锁,写完后可能有新的数据加入 cache,所以需要检查 cache 是否完全写下并重试。
/* Make sure all the caches are synced. */
for (i = 0; i < ib_vector_size(cache->indexes); ++i) {
fts_index_cache_t *index_cache;
index_cache =
static_cast<fts_index_cache_t *>(ib_vector_get(cache->indexes, i));
if (index_cache->index->to_be_dropped ||
fts_sync_index_check(index_cache)) {
continue;
}
goto begin_sync;
}
提交
fts_sync` -> `fts_sync_commit
- 数据写入后
fts_cmp_set_sync_doc_id更新 doc_id,持久化 FTS 索引插入的内容 fts_sync_add_deleted_cache把 cache 中删除的 doc_id(deleted_doc_id)插入 FTS__DELETED_CACHE。但是`deleted_doc_id`没有任何插入,所以这个表是没有用的。推测这个结构的本意是在事务过程中删除的 docid 直接加入 cache,用来确保 FTS 不会查到删除的数据。 fts_cache_clear清空 cache
/* After each Sync, update the CONFIG table about the max doc id
we just sync-ed to index table */
error = fts_cmp_set_sync_doc_id(sync->table, sync->max_doc_id, FALSE,
&last_doc_id);
/* Get the list of deleted documents that are either in the
cache or were headed there but were deleted before the add
thread got to them. */
if (error == DB_SUCCESS && ib_vector_size(cache->deleted_doc_ids) > 0) {
error = fts_sync_add_deleted_cache(sync, cache->deleted_doc_ids);
}
/* We need to do this within the deleted lock since fts_delete() can
attempt to add a deleted doc id to the cache deleted id array. */
fts_cache_clear(cache);
DEBUG_SYNC_C("fts_deleted_doc_ids_clear");
fts_cache_init(cache);
rw_lock_x_unlock(&cache->lock);
if (error == DB_SUCCESS) {
fts_sql_commit(trx);
安全性
关于 cache 同步有下面几个事实:
- 一次完整的 sync 是一个(大)事务,保证原子性和一致性
- sync 结束时把最大 doc_id 写入 config 表 sync_doc_id 行
- 一个文本在插入 cache 时全程拿锁
- sync 过程中虽然可以放锁,但是在最后阶段检查 cache 内容时全程持有锁,保证 cache 全部完成 sync
- 表初始化时,总是会检查 config 表中的 sync_doc_id,并把表 sync_doc_id 后的所有内容加入 cache
这意味着:
- 任意一个文本的索引项,一定是完全在磁盘上或完全不在磁盘上
- config 表中的 sync_doc_id 不小于已索引的任意文本 doc_id
- 正常运行时,node 上的 sync 标记保证一个 node 只写入一次,索引中的 doc_id 不会重复
- crash 后,cache 的内容是从 sync_doc_id 之后加载的,内存中一定不会出现已 sync 的 doc_id
- 开表后,新增文本的 doc_id 总是大于 1. 磁盘上的任意文本 2. 表中尚未 sync 且尚未删除的文本,新增 doc_id 不会和已有的重复,内存中同一 doc_id 不会出现在多个 node 中
- 磁盘上的 node 是从 cache 中 node 写下的,磁盘和内存中的 node 要么完全相同,要么完全不同。完全相同的 node 仅限同步过程中已写入磁盘的 node,在脏读隔离级别下对 FTS 可见。
bug
由于新 doc_id 的分配和加入 cache 是两个操作,有可能出现
- 插入文本 1,产生新 doc_id_1
- 插入文本 2,产生更大的 doc_id_2
- 2 提交,加入 cache
- 同步,doc_id_2 写入磁盘
- 1 提交,尚未同步
- crash
此时 config 表中的 sync_doc_id >= doc_id_2,而 docid1 尚未写入索引,且再也不会加入 cache。解决这个问题需要 doc_id 的产生和加入 cache 原子。
Optimize
FTS 索引删除不直接写入索引表,而是写入 FTS_
fts_optimize_thread线程定期对已打开的包含 FTS 索引的表做 optimize,打开的表通过fts_optimize_{add, remove}_table追踪。- 用户执行
OPTIMIZE TABLE
常规 optimize 路径 fts_optimize_thread -> fts_optimize_table_bk -> fts_optimize_table -> fts_optimize_indexes -> fts_optimize_index
准备
fts_optimize_create_deleted_doc_id_snapshot拷贝 FTS__DELETED 到 FTS_ _BEING_DELETED,拷贝 FTS_ _DELETED_CACHE 到 FTS_ _BEING_DELETED_CACHE fts_optimize_read_deleted_doc_id_snapshot从 BEING 表读需要删除的 doc_id。这里的代码可能有 bug?
optim->fts_common_table.suffix = FTS_SUFFIX_BEING_DELETED;
/* Read the doc_ids to delete. */
error = fts_table_fetch_doc_ids(optim->trx, &optim->fts_common_table,
optim->to_delete);
if (error == DB_SUCCESS) {
optim->fts_common_table.suffix = FTS_SUFFIX_BEING_DELETED;
/* Read additional doc_ids to delete. */
error = fts_table_fetch_doc_ids(optim->trx, &optim->fts_common_table,
optim->to_delete);
}
删除
- 从索引读入分词列表
fts_optimize_index -> fts_optimize_index_read_words -> fts_index_fetch_words -> fts_fetch_index_words 启动事务访问索引表的全部分片,读分词同时做块压缩。如果之前已经做过 optimize,上一次优化到的分词会记录在 CONFIG 表内last_optimized_word行,这次优化会从这个分词之后开始。
- 优化
fts_zip_read_word` 解压,`fts_optimize_words` 遍历分词-> `fts_optimize_compact` -> `fts_optimize_word` 拷贝 ilist -> `fts_optimize_node` 跳过已删除的 doc_id -> `fts_optimize_encode_node`拷贝 `fts_node_t
fts_optimize_compact 会检查 optimize 所花的时间,超过 CONFIG 表中FTS_OPTIMIZE_LIMIT_IN_SECS值后停止当前 optimize。当前代码是 180 秒。
- 写入
fts_optimize_write_word删除索引中原来的记录,然后重新插入 - 如果所有分词都优化了,重置 CONFIG 表内的
last_optimized_word行
清理
如果所有分析都优化了,fts_optimize_purge_snapshot 从 DELETE(CACHE) 表删除 BEING_DELETE(CACHE) 表中的内容,然后清空 BEING_DELETE(_CACHE) 表
安全性
开始前从 DELETED 表拷贝产生快照 BEING_DELETED,这个表是这一轮 optimize 优化的 doc_id,所有分词都优化完后才清空这个表。每次开始 optimize 时首先检查这个表非空,保证一轮 optimize 中每一次总是优化同一组 doc_id。
每个分词优化完后写入 CONFIG 表,保证下一次从同一位置开始优化
如果开始 optimize 时,DELETED 表中有尚未同步的 doc_id,拷贝进入了 BEING_DELETED 表,optimize 后才同步,相应的 doc_id 就留在索引内,删不掉?
查询
fts_ast_visitor 遍历 AST
└ fts_query_visitor (回调函数) 处理节点
├ fts_ast_visit_sub_exp → fts_ast_visitor
│ FTS_AST_SUBEXP_LIST: 括号包围的子查询例如 'exp (subexp)'
├ fts_query_execute
│ FTS_AST_TERM: 简单查询对应的常规节点, 通常是一个分词, 可能带有 + - > < 操作符
│ ├ fts_query_union 或
│ ├ fts_query_intersect 且
│ └ fts_query_difference 非
│ └ fts_index_fetch_nodes 按分词查倒排索引
│ └ fts_parse_sql
│ ┆ InnoDB SQL 解析器
│ └ fts_query_index_fetch_nodes (回调函数)
│ └ fts_query_read_node 解析倒排索引的一行数据
│ └ fts_query_filter_doc_ids 处理 doc_id 和位置信息
│ └ fts_query_process_doc_id 处理结果集中单个匹配
│ ├ fts_query_union_doc_id 或
│ ├ fts_query_intersect_doc_id 且
│ ├ fts_query_remove_doc_id 非
│ └ fts_query_change_ranking 更改权重
└ fts_query_phrase_search
FTS_AST_PARSER_PHRASE_LIST/FTS_AST_TEXT: 词组搜索, " " 包围的内容
└ fts_index_fetch_nodes
JOIN::optimize_fts_query` -> ... -> `fts_query
- 获取删除的 doc_id
fts_table_fetch_doc_id,访问 FTS__DELETED,FTS_ _DELETED_CACHE 和内存 cache
query.fts_common_table.suffix = FTS_SUFFIX_DELETED;
/* Read the deleted doc_ids, we need these for filtering. */
error = fts_table_fetch_doc_ids(NULL, &query.fts_common_table, query.deleted);
if (error != DB_SUCCESS) {
goto func_exit;
}
query.fts_common_table.suffix = FTS_SUFFIX_DELETED_CACHE;
error = fts_table_fetch_doc_ids(NULL, &query.fts_common_table, query.deleted);
if (error != DB_SUCCESS) {
goto func_exit;
}
/* Get the deleted doc ids that are in the cache. */
fts_cache_append_deleted_doc_ids(index->table->fts->cache,
query.deleted->doc_ids);
- 解析查询串,生成语法树
fts_query_parse。FTS 查询支持自然语言模式和布尔模式,自然语言模式返回匹配到任意一个分词的文本,布尔模式支持复杂操作符和嵌套的语句。实现上两种模式仅在词法分析上有区别,见 fts0tlex.l 和 fts0blex.l。 - 执行查询。
fts_ast_visit遍历语法树 ->fts_query_visitor每个节点- 匹配简单的单词
fts_query_execute,按照指定的操作符查询、合并结果- 查询 cache
fts_find_index_cachefts_cache_find_word fts_index_fetch_nodes用分词查 FTS 索引fts_query_index_fetch_nodes读查询结果 ->fts_query_read_node->fts_query_index_fetch_nodes解析 doc_id 和位置,加入结果中 ->fts_query_process_doc_id->fts_query_{union, intersect. remove}_docid,fts_query_change_ranking按照操作符做结果集合的交、并等操作。fts_query_add_word_to_document把匹配的分词加到对应的文本上,更新文本 rank。
- 查询 cache
- 匹配词组
fts_query_phrase_search- 展开词组
fts_query_phrase_split,然后类似于上面的流程单独匹配每个分词, - 匹配词组/临近词组(
"apple banana"/"apple banana" @2)需要确认文本中出现全部分词,并且连续或在给定的距离内(@2)。临近词组不匹配 stopword,词组匹配检查 stopword fts_phrase_or_proximity_search滤掉没有全部匹配的 doc_id,确认文本中出现全部分词(不包含检查 stopword)- 临近词组(类似于
"apple banana" @2)获得极小匹配位置范围(字节)fts_proximity_get_positions,然后检查范围内的分词数量,确认分词在给定的单词距离内fts_query_is_in_proximity_range。 - 普通词组检查词组和文本匹配
fts_query_search_phrase->fts_query_match_document,stopword 在这一步检查。
- 展开词组
- 匹配简单的单词
- 扩展查询
fts_expand_query,用第一次查询的到的文本再次查询。分词fts_query_expansion_fetch_doc后,去掉初次查询使用的分词,再次查询fts_query_union - 计算 idf
fts_query_calculate_idf。如果共有N个文本,分词t出现在n_t个文本中,IDF(inverse document frequency)公式\operatorname{idf}_{t} = log{10}\frac{N}{n_t},包含分词文本越少,IDF 越大
if (word_freq->doc_count > 0) {
if (total_docs == word_freq->doc_count) {
/* QP assume ranking > 0 if we find
a match. Since Log10(1) = 0, we cannot
make IDF a zero value if do find a
word in all documents. So let's make
it an arbitrary very small number */
word_freq->idf = log10(1.0001);
} else {
word_freq->idf = log10(total_docs / (double)word_freq->doc_count);
}
}
- 排除已经删除的文本,计算权重
fts_query_get_result->fts_query_prepare_result->fts_query_calculate_ranking。如果分词t在文本d中出现\operatorname{tf}{t,d}次,分词对文本权重的贡献是\operatorname{tf-idf}{t, d} = \operatorname{tf}_{t, d} \times \operatorname{idf}_t^2,文本包含分词的数量越大,权重越大。可以参考 tf-idf - Wikipedia
weight = (double)doc_freq->freq * word_freq->idf;
ranking->rank += (fts_rank_t)(weight * word_freq->idf);
drop
row_drop_table_for_mysql
- 先锁 FTS 表,包括索引表和其他辅助表
fts_lock_all_aux_tables,然后 drop 辅助表。 - drop 所有 FTS 表
row_drop_ancillary_fts_tables->fts_drop_tables->fts_drop_common_tables/ (fts_drop_all_index_tables->fts_drop_index_tables) ->fts_drop_table-> 递归row_drop_table_for_mysql dd_drop_fts_table