InnoDB 二级索引 B+ 树的 Key 是什么?
Author: 王炳杰(唤舟)
导言
MySQL InnoDB 采用索引组织表存储数据,对于聚簇索引,Key 是主键字段,Value 是行数据。对于二级索引,普遍认知是它包含了二级索引字段和主键字段,但这里存在一个细节问题,二级索引 B+ 树的 Key 是什么?该问题可以从这两个角度展开思考:
- 聚簇索引是 unique 的,但二级索引并不一定是,非 unique 的二级索引如何实现?
- InnoDB 使用 MVCC 来避免读写冲突:当一个更新操作只改变了主键的值(pkv,primary key value)而未改变二级索引字段值(skv,secondary key value)的时候,聚簇索引上表现为删除 + 插入,此时二级索引该如何维护呢?update in place 是不合理的
实际上,InnoDB 二级索引的 Key 是二级索引字段 + 不在其中的主键字段,这样能简单直接地解决上述问题。接下来通过源码一探究竟
二级索引的结构
已有两篇内核月报文章有相关的分析:
本文主要拓展两点:
- 索引结构是怎么定义的?(
index_def_tanddict_index_t) - 二级索引中间节点和叶子节点的 record 是什么样的?(包括 bulk load 和 insert 路径)
结构
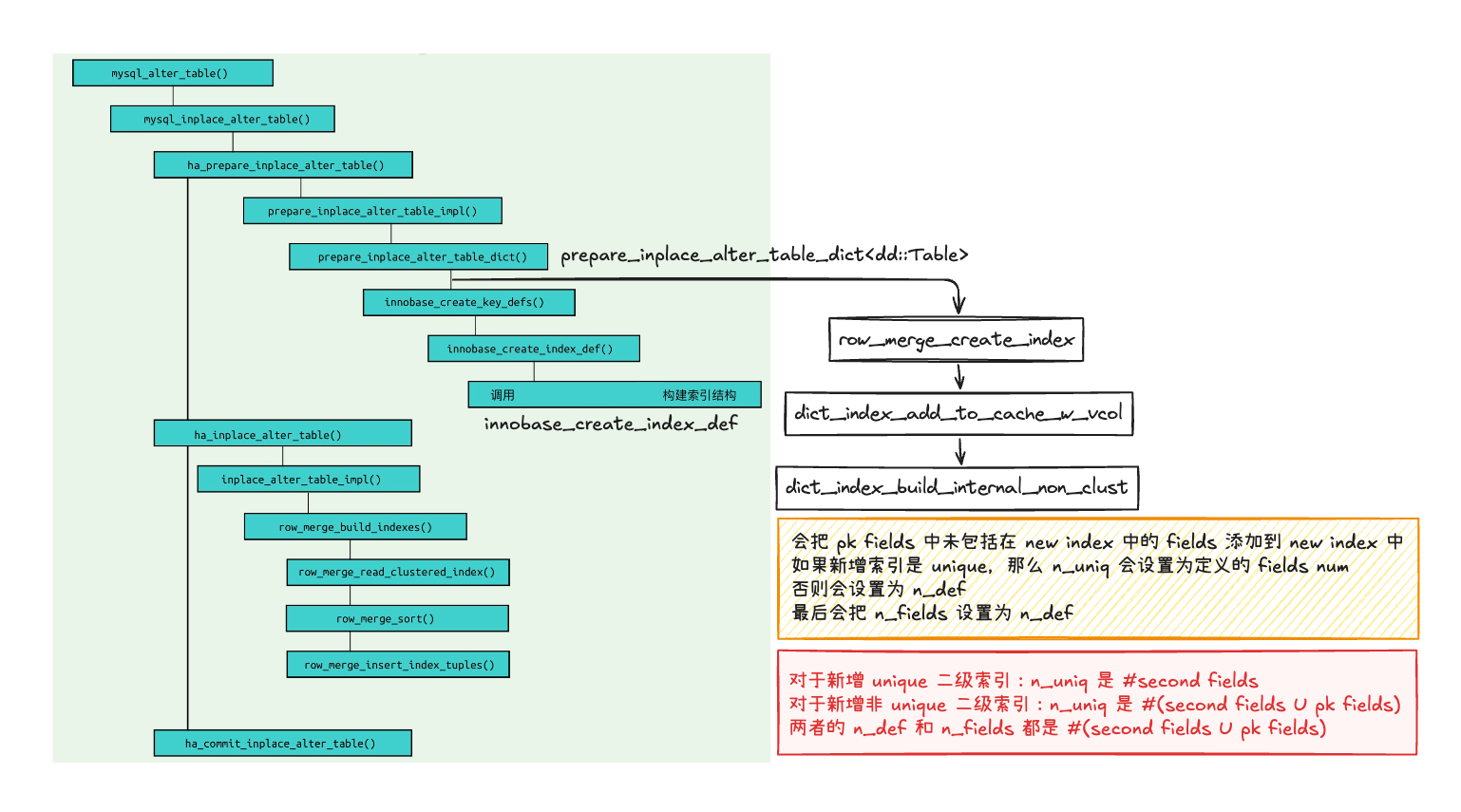
这里对文 1 中的一张图进行了补充:
innobase_create_index_def->index_def_t(该结构文 1 中进行了描述)dict_index_build_internal_non_clust->dict_index_t
struct dict_index_t {
...
unsigned n_uniq : 10; /*!< number of fields from the beginning
which are enough to determine an index
entry uniquely */
unsigned n_def : 10; /*!< number of fields defined so far */
unsigned n_fields : 10; /*!< number of fields in the index */
unsigned n_nullable : 10; /*!< number of nullable fields */
dict_field_t *fields; /*!< array of field descriptions */
// 和 n_def 是一一对应的,和 tuple 里的 fields 也是一一对应的
...
}
源码:
dict_index_t *dict_index_build_internal_non_clust(...)
{
// 创建一个新的 dict_index_t
new_index = dict_mem_index_create(...);
// 把二级索引字段拷贝到 new_index 中
dict_index_copy(new_index, index, table, 0, index->n_fields);
// 标记二级索引字段
for (i = 0; i < new_index->n_def; i++) {
field = new_index->get_field(i);
...
indexed[field->col->ind] = TRUE;
}
// 把未被标记的主键字段添加到 new index 中
for (i = 0; i < clust_index->n_uniq; i++) {
field = clust_index->get_field(i);
if (!indexed[field->col->ind]) {
dict_index_add_col(new_index, table, field->col, ...);
indexed[field->col->ind] = TRUE;
}
...
}
...
if (dict_index_is_unique(index)) {
// unique 二级索引的 n_uniq 值为 #second fields
new_index->n_uniq = index->n_fields;
} else {
// 非 unique 二级索引的 n_uniq 值为 #(second fields U pk fields)
new_index->n_uniq = new_index->n_def;
}
// 二级索引的 n_fields 值为 #(second fields U pk fields)
new_index->n_fields = new_index->n_def;
return (new_index);
}
另外,对比 dict_index_build_internal_clust 函数可以发现二级索引并未添加 DB_ROW_ID、DB_TRX_ID 和 DB_ROLL_PTR 这几列
这里从 n_uniq 和 n_fields 的取值上已经初见端倪
二级索引叶子节点
如图所示是二级索引 bulk load 流程(左图)和 normal insert 流程(右图)中数据行的类型转换图
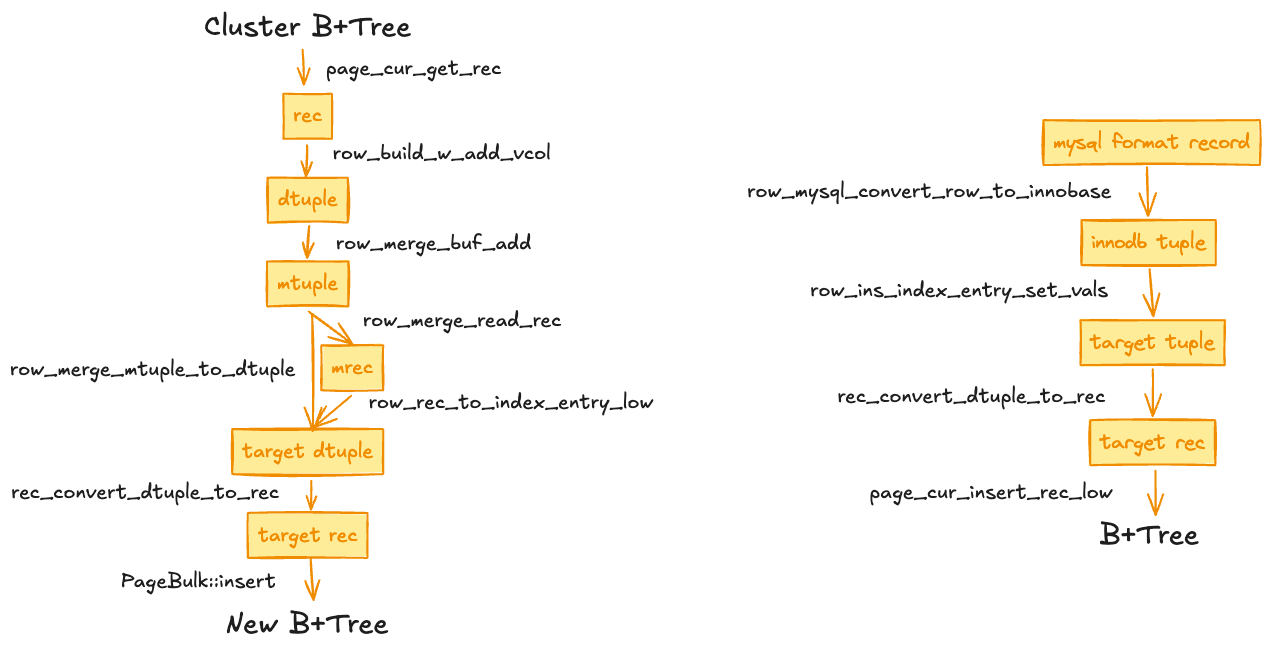
无论是 bulk load 还是 insert 起初拿到的都是一行完整的数据,它们会通过下面代码块中的这段逻辑,从完整的 row 中提取一些字段来填充好二级索引的 entry:
- bulk load:
row_merge_buf_add - normal insert:
row_ins_index_entry_set_vals
n_fields = dict_index_get_n_fields(index); // 二级索引的 n_fields
for (i = 0; i < n_fields; i++) {
...
field = dtuple_get_nth_field(entry, i)
ind_field = index->get_field(i); // 每个 field
col = ind_field->col;
col_no = dict_col_get_no(col); // 拿到 col num
row_field = dtuple_get_nth_field(row, col_no); // 从完整的 row 中通过 col num 拿到对应的 field
dfield_copy(field, row_field); // or dfield_set_data
...
}
后续会通过 rec_convert_dtuple_to_rec 构造出 physical records,过程中会基于 rec,往前填充变长字段长度列表、null bitmap、 record header 信息(包括 info flags、status 等),往后填充各字段的值,大致逻辑如下:
...
rec = buf + extra_size; // 指向第一个 field value
...
ulint null_mask = 1;
nulls = rec - (REC_N_NEW_EXTRA_BYTES + 1); // 指向 null bitmap 的 last byte
...
lens = nulls - UT_BITS_IN_BYTES(n_null); // 指向变长字段长度列表的 last byte
memset(lens + 1, 0, nulls - lens); /* clear the SQL-null flags */
...
end = rec;
for (i = 0; i < n_fields; i++) {
field = &fields[i];
type = dfield_get_type(field);
len = dfield_get_len(field);
...
if (dfield_is_null(field)) {
*nulls |= null_mask;
null_mask <<= 1;
continue;
}
null_mask <<= 1;
...
*lens-- = (byte)len;
...
if (len > 0) memcpy(end, dfield_get_data(field), len);
end += len;
}
...
rec_set_info_and_status_bits(rec, info_bits)
...
可以看到 physical record 完全基于 tuple 进行构造,下图是二级索引叶子节点 record 结构图:
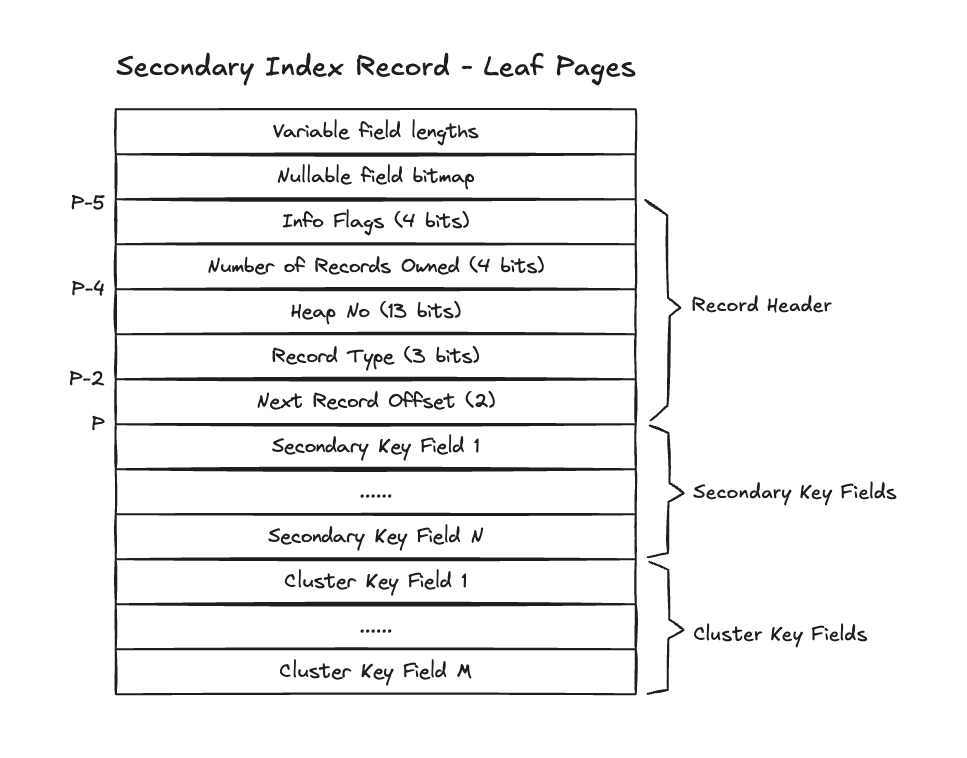
从 leaf page record 的角度来看,难以区分 key 到底是什么
二级索引中间节点
中间节点记录的也是一个个的 record,称为 node ptr,看一下它是如何构建的:
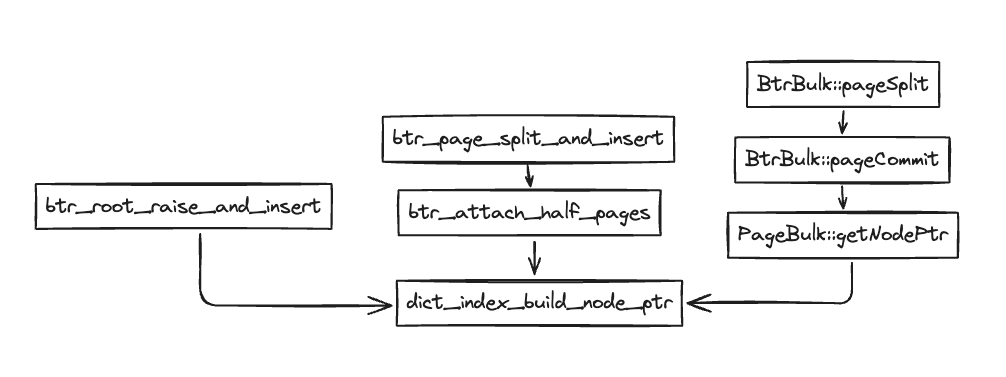
无论是 bulk load 还是 insert,殊途同归,都走到了 dict_index_build_node_ptr 这里:
/** Builds a node pointer out of a physical record and a page number.
@return own: node pointer */
dtuple_t *dict_index_build_node_ptr(const dict_index_t *index, ...)
{
// 创建一个有 n_unique + 1 个字段的 tuple
// 注意看下面的函数,这里二级索引并非用了 n_uniq 值而是 n_fields 值
n_unique = dict_index_get_n_unique_in_tree_nonleaf(index);
tuple = dtuple_create(heap, n_unique + 1);
...
// 最后一个字段是 4B 的 page_no,类型为 DATA_SYS_CHILD | DATA_NOT_NULL
mach_write_to_4(buf, page_no);
field = dtuple_get_nth_field(tuple, n_unique);
dfield_set_data(field, buf, 4);
dtype_set(dfield_get_type(field), DATA_SYS_CHILD, DATA_NOT_NULL, 4);
// 设置其他字段
rec_copy_prefix_to_dtuple(tuple, rec, index, n_unique, heap);
...
}
/** Gets the number of fields in the internal representation of an index
which uniquely determine the position of an index entry in the index, if
we also take multiversioning into account.
@return number of fields */
ulint dict_index_get_n_unique_in_tree(const dict_index_t *index)
{
// 聚簇索引返回 index->n_uniq
if (index->is_clustered()) {
return (dict_index_get_n_unique(index));
}
// 二级索引返回 index->n_fields
return (static_cast<uint16_t>(dict_index_get_n_fields(index)));
}
可以看到,对于二级索引来说,node ptr 有 n_fields + 1 个字段,最后一个字段是 child page no。下图是二级索引中间节点 record 结构图:
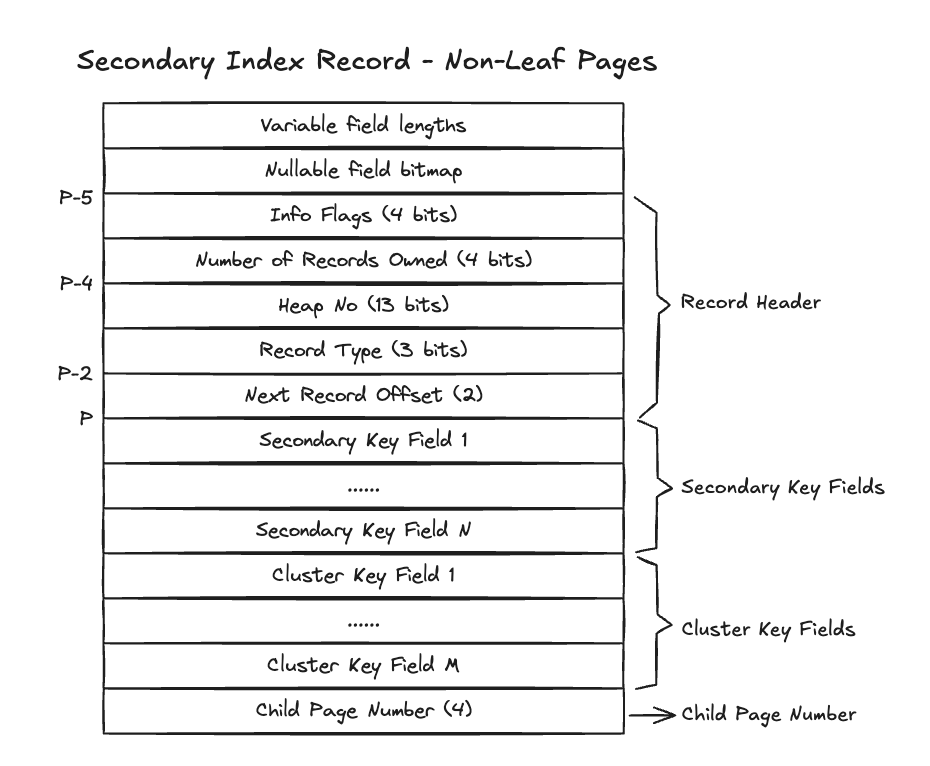
由此可见,InnoDB 二级索引 B+ 树的 Key 是二级索引字段 + 不在其中的主键字段
为什么 Key 要组织成这样?一个显而易见的好处是能够简单自然地支持非 unique 的二级索引,因为主键字段的加入保证了 Key 的唯一性,从而不需要支持 duplicate key
那么问题来了,是不是 unique 的二级索引就不必这样了?并不是,通过源码可以看到,在 dict_index_build_node_ptr 的时候,对于二级索引,其字段数量永远是 n_fields + 1,并不会因为是否 unique 而有所区分
所以,把主键字段加入二级索引 Key 还有别的原因
二级索引的更新
回到我们提出的第二个思考点,来看如下四种更新的情况:
| case | cluster index | secondary index (assume skf as key) |
secondary index | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | only change pkv | d + i | u | d + i |
| 2 | only change skv | u | d + i | d + i |
| 3 | change both | d + i | d + i | d + i |
| 4 | change no | u | do nothing | do nothing |
PS:
- d 表示 delete,i 表示 insert,u 表示 update “in-place”
- 这里的 change or not 只考虑 pkv 和 skv,所以 case 4 指的是更新了非主键和非该二级索引字段外的其他字段
聚簇索引上:
- 如果更新了主键(case 1 & case 3),会执行为 delete + insert(
row_upd_clust_rec_by_insert),这是因为要维护 B+ 树的 order,同时支持 MVCC,”old” read 能看到更新前的 record; - 如果没有更新主键(case 2 & case 4),就试图 update “in-place”(
row_upd_clust_rec)(不一定是 physical in-place,重点是保持 order,可能会导致 split)
对二级索引来说,它的更新操作也要考虑 order + MVCC,所以:
- 对于更新了二级索引字段值的情况(case 2 & case 3),其表现为 delete + insert
- 对于什么都没更新的情况(case 4),其保持不变
- 对于只更新了主键值的情况(case 1):如果 key 只是二级索引字段的话,此时只能试图 update in-place,虽然它满足了 order,但是没满足 MVCC,如果一个 “old” read 命中了该二级索引,会找不到更新前的 record 版本,从而导致问题
分析源码,对二级索引的更新流程如下:
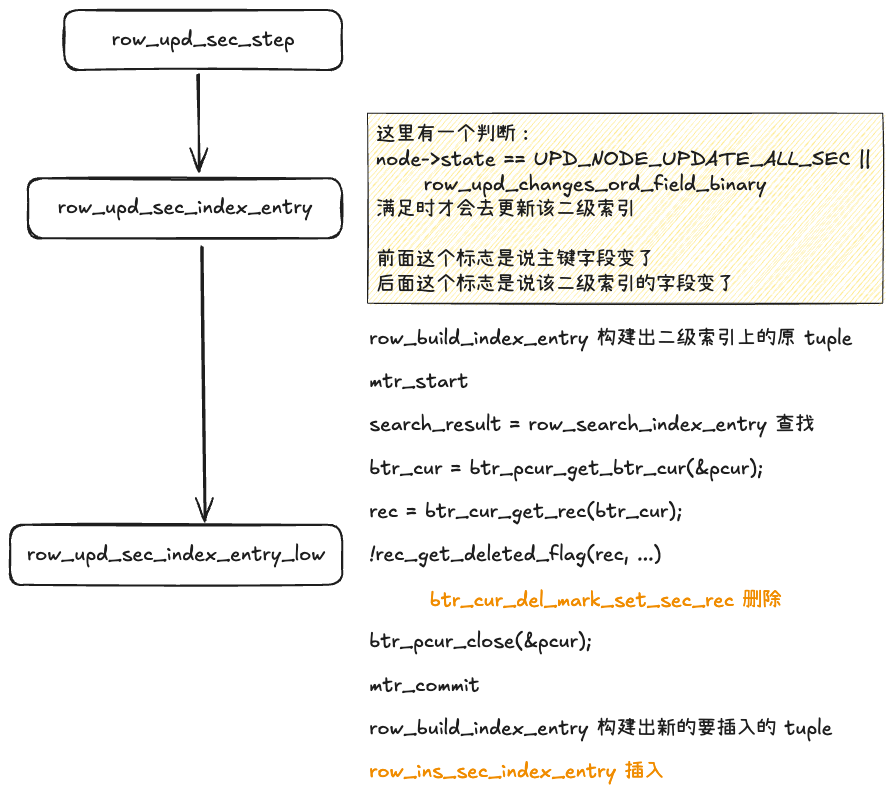
可以看到其基本逻辑是:对二级索引的更新总是先删除后插入。前面已经确认了 Key 的结构,那么只要更新了 pkv 或者 skv,二级索引上都会表现为删除 + 插入。如果有 “old” read,是能够查到原来的 record 的,满足一致性读
这种情况也可以拓展到其他 DML 操作上,比如:
- 删除后插入一行新的记录,其 skv 和之前一样,但是 pkv 不一样,那么二级索引上应该保留两个 record 的,旧的 record mark delete
- 一次 update 把 skv1 修改为 skv2,二级索引上同时存着这两条 record,此时又插入了 skv1,或者把 skv3 更新为了 skv1
- 等等
这一点总的来说是:
- 为了保证 MVCC,二级索引需要保留一些被删掉的 records
- 这样会导致即便是 unique 二级索引,也会出现相同 skv 的多个 records。此时这些 records 的 pkv 一定是不同的,并且最多只有一个 record 没有被 mark delete
- 所以仍然需要补充 primary key fields 来保证 B+ 树 Key 唯一,快速定位 target record
总结
本文通过分析相关源码验证了:InnoDB 二级索引的 Key 是二级索引字段 + 不在其中的主键字段
为什么这么实现?文中给出两个原因:一是支持非 unique 二级索引,二是支持 MVCC。两者的核心点其实都是:在二级索引 B+ 树上,二级索引字段不足以唯一标识一个 record,需要补充主键字段后才能唯一标识